The pro-apoptotic paradox: the BH3-only protein Bcl-2 interacting killer (Bik) is prognostic for unfavorable outcomes in breast cancer
- PMID: 27120789
- PMCID: PMC5078093
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.8924
The pro-apoptotic paradox: the BH3-only protein Bcl-2 interacting killer (Bik) is prognostic for unfavorable outcomes in breast cancer
Abstract
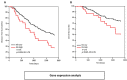
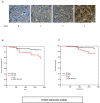
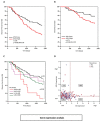
Breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer-associated deaths in women worldwide. Clinical biomarkers give information on disease progression and identify relevant biological pathways. A confounding factor that uncouples markers from disease outcome is the ability of tumor cells to mutate and evade clinical intervention. Therefore, we focussed on apoptotic genes that modulate tumor regression. Using gene and tissue microarray analyses, we identified an association of Bcl-2 interacting killer (Bik) with poor breast cancer prognosis. Bik prognostic ability was independent of Estrogen Receptor/Progesterone Receptor and Her2 status. Additionally, Bik was independent of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, Mcl-1 and Bcl-w suggesting a complex mechanism of tumor promotion identified by Bik high tumors. Bik also stimulates autophagy, which can contribute to enhanced tumor fitness. We found a significant association between the autophagy marker ATG5 and Bik. Combined high expression level of ATG5 and Bik was a stronger predictor of outcome than either alone. Thus, our study identifies Bik as a novel, independent prognostic biomarker for poor outcomes in breast cancer and suggests that Bik-mediated autophagy contributes to disease recurrence.
Keywords: BH3-only proteins; Bcl-2 interacting killer; BiK; autophagy; breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest Author contributions VP and ISG designed the study; VP, DG and LV performed experiments and collected data; VP and Jo Ha performed statistical analysis; SD, JRM and JHugh provided expert opinions on oncology and pathology; VP and ISG wrote the manuscript and all authors provided input.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Novel mechanism of anti-apoptotic function of 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein (GRP78): endocrine resistance factor in breast cancer, through release of B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) from BCL-2-interacting killer (BIK).J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 22;286(29):25687-96. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.212944. Epub 2011 May 26. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21622563 Free PMC article.
-
Breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 miRNA profile expression after BIK interference: BIK involvement in autophagy.Tumour Biol. 2016 May;37(5):6749-59. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4494-8. Epub 2015 Dec 10. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26662110
-
Correlation of the protein expression of GRP78 and BIK/NBK with prognostic markers in patients with breast cancer and neoadjuvant chemotherapy.J Obstet Gynaecol. 2020 Apr;40(3):419-426. doi: 10.1080/01443615.2019.1652886. Epub 2019 Oct 22. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2020. PMID: 31635499
-
The prognostic value of long noncoding RNA HOTTIP on clinical outcomes in breast cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 24;8(4):6833-6844. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14304. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28036281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BIK, the founding member of the BH3-only family proteins: mechanisms of cell death and role in cancer and pathogenic processes.Oncogene. 2008 Dec;27 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S20-9. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.40. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 19641504 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ring finger protein 6 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation by stabilizing estrogen receptor alpha.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 21;8(12):20103-20112. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15384. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28223545 Free PMC article.
-
BIK drives an aggressive breast cancer phenotype through sublethal apoptosis and predicts poor prognosis of ER-positive breast cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jun 11;11(6):448. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2654-2. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32528057 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA TUG1 knockdown prevents neurons from death to alleviate acute spinal cord injury via the microRNA-338/BIK axis.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):5566-5582. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1966258. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34517787 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of AQP5 gene silencing on proliferation, migration and apoptosis of human glioma cells through regulating EGFR/ERK/ p38 MAPK signaling pathway.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 13;8(24):38444-38455. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16461. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28404978 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy is associated with a robust specific transcriptional signature in breast cancer subtypes.Genes Cancer. 2020 Oct 6;11(3-4):154-168. doi: 10.18632/genesandcancer.208. eCollection 2020 Dec 31. Genes Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33488952 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. International journal of cancer. 2015;136:E359–386. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J SI, Ervik M, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11. GLOBOCAN 2012. 2013;v10 - PubMed
-
- Van Poznak C, Somerfield MR, Bast RC, Cristofanilli M, Goetz MP, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Hicks DG, Hill EG, Liu MC, Lucas W, Mayer IA, Mennel RG, Symmans WF, Hayes DF, Harris LN. Use of Biomarkers to Guide Decisions on Systemic Therapy for Women With Metastatic Breast Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. Journal of clinical oncology. 2015;33:2695–2704. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

