ImiRP: a computational approach to microRNA target site mutation
- PMID: 27122020
- PMCID: PMC4848830
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-016-1057-y
ImiRP: a computational approach to microRNA target site mutation
Abstract
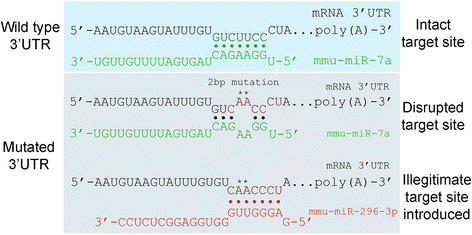
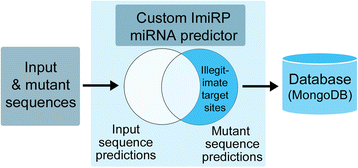
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small ~22 nucleotide non-coding RNAs that function as post-transcriptional regulators of messenger RNA (mRNA) through base-pairing to 6-8 nucleotide long target sites, usually located within the mRNA 3' untranslated region. A common approach to validate and probe microRNA-mRNA interactions is to mutate predicted target sites within the mRNA and determine whether it affects miRNA-mediated activity. The introduction of miRNA target site mutations, however, is potentially problematic as it may generate new, "illegitimate sites" target sites for other miRNAs, which may affect the experimental outcome. While it is possible to manually generate and check single miRNA target site mutations, this process can be time consuming, and becomes particularly onerous and error prone when multiple sites are to be mutated simultaneously. We have developed a modular Java-based system called ImiRP (Illegitimate miRNA Predictor) to solve this problem and to facilitate miRNA target site mutagenesis.
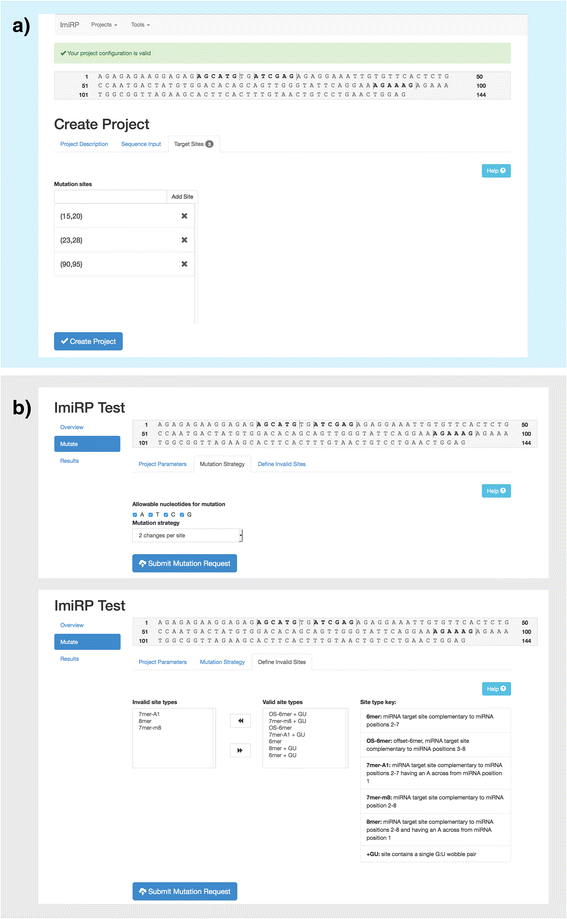
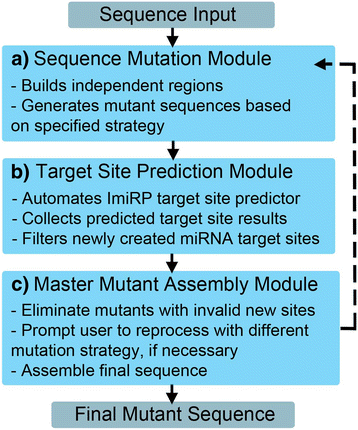
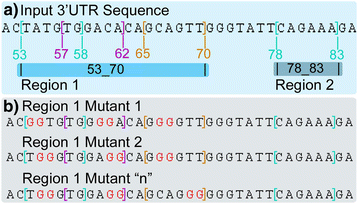
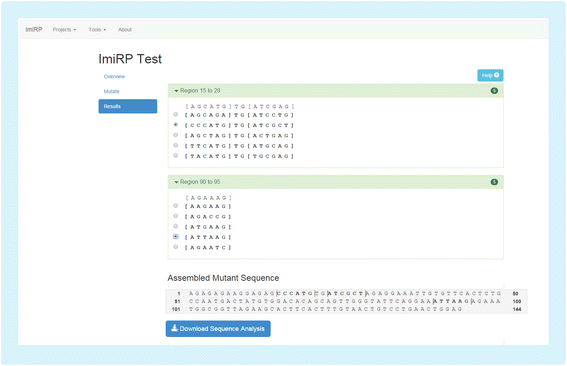
Results: The ImiRP interface allows users to input a sequence of interest, specify the locations of multiple predicted target sites to mutate, and set parameters such as species, mutation strategy, and disallowed illegitimate target site types. As mutant sequences are generated, ImiRP utilizes the miRBase high confidence miRNA dataset to identify illegitimate target sites in each mutant sequence by comparing target site predictions between input and mutant sequences. ImiRP then assembles a final mutant sequence in which all specified target sites have been mutated.
Conclusions: ImiRP is a mutation generator program that enables selective disruption of specified miRNA target sites while ensuring predicted target sites for other miRNAs are not inadvertently created. ImiRP supports mutagenesis of single and multiple miRNA target sites within a given sequence, including sites that overlap. This software will be particularly useful for studies looking at microRNA cooperativity, where mutagenesis of multiple microRNA target sites may be desired. The software is available at imirp.org and is available open source for download through GitHub ( https://github.com/imirp ).
Keywords: Automation; MicroRNA; Mutagenesis; Seed Sequence; Software; Target Site.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA binding sites in C. elegans 3' UTRs.RNA Biol. 2014;11(6):693-701. doi: 10.4161/rna.28868. Epub 2014 Apr 25. RNA Biol. 2014. PMID: 24827614 Free PMC article.
-
The human transcriptome is enriched for miRNA-binding sites located in cooperativity-permitting distance.RNA Biol. 2013 Jul;10(7):1125-35. doi: 10.4161/rna.24955. Epub 2013 May 9. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23696004 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome-wide prediction of miRNA targets in human and mouse using FASTH.PLoS One. 2009 May 29;4(5):e5745. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005745. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19478946 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA Targeting: Growing beyond the Seed.Trends Genet. 2019 Mar;35(3):215-222. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2018.12.005. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Trends Genet. 2019. PMID: 30638669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macros in microRNA target identification: a comparative analysis of in silico, in vitro, and in vivo approaches to microRNA target identification.RNA Biol. 2014;11(4):324-33. doi: 10.4161/rna.28649. Epub 2014 Apr 2. RNA Biol. 2014. PMID: 24717361 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
microRNA-92a regulates the expression of aphid bacteriocyte-specific secreted protein 1.BMC Res Notes. 2019 Sep 30;12(1):638. doi: 10.1186/s13104-019-4665-6. BMC Res Notes. 2019. PMID: 31564246 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in Cancer Biology and Therapy from a Systems Biology Perspective.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1385:1-22. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-08356-3_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 36352209 Review.
-
Human MicroRNAs Attenuate the Expression of Immediate Early Proteins and HCMV Replication during Lytic and Latent Infection in Connection with Enhancement of Phosphorylated RelA/p65 (Serine 536) That Binds to MIEP.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 2;23(5):2769. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052769. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269913 Free PMC article.
-
SNPs in microRNA target sites and their potential role in human disease.Open Biol. 2017 Apr;7(4):170019. doi: 10.1098/rsob.170019. Open Biol. 2017. PMID: 28381629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of PD-L1 expression by miR-140/142/340/383 and oncogenic activation of the OCT4-miR-18a pathway in cervical cancer.Oncogene. 2018 Sep;37(39):5257-5268. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0347-4. Epub 2018 May 31. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29855617 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lewis B, Shih I, Jones-Rhoades M, Bartel D. Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell. 2003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

