Regorafenib-Related Myocardial Injury during Atrial Fibrillation
- PMID: 27122956
- PMCID: PMC4816924
- DOI: 10.6515/acs20150629b
Regorafenib-Related Myocardial Injury during Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
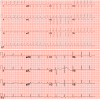
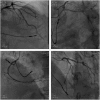
Multikinase inhibitors with an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor effect have been reported to increase the risk of myocardial infarction or ischemia. We have presented the case of a 72-year-old male who had a metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor for which he received targeted therapy and who was admitted to our hospital for recurrent episodes of myocardial injury during atrial fibrillation. Coronary angiography showed insignificant coronary artery stenosis. We also reviewed the incidence of cardiovascular events in patients receiving regorafenib, and the current understanding of the mechanism of targeted therapy-induced myocardial ischemia/infarction.
Key words: Multikinase inhibitor • Myocardial infarction • Myocardial ischemia • Vascular endothelial growth factor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Suspected Case of Acute Embolic Myocardial Infarction Following Direct-Current Cardioversion of Atrial Fibrillation.Am J Case Rep. 2018 Nov 2;19:1306-1310. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.911469. Am J Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 30385736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Agranulocytosis and acute coronary syndrome in apathetic hyperthyroidism].Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2003 May-Jun;131(5-6):249-53. doi: 10.2298/sarh0306249i. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2003. PMID: 14692133 Serbian.
-
Atrial fibrillation, progression of coronary atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction.Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2017 Mar;24(4):373-381. doi: 10.1177/2047487316679265. Epub 2016 Nov 12. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 27837151
-
Antiplatelet therapy for stable coronary artery disease in atrial fibrillation patients taking an oral anticoagulant: a nationwide cohort study.Circulation. 2014 Apr 15;129(15):1577-85. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.004834. Epub 2014 Jan 27. Circulation. 2014. PMID: 24470482
-
Regorafenib: a novel multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor for colorectal cancer and gastrointestinal stromal tumors.Ann Pharmacother. 2013 Dec;47(12):1685-96. doi: 10.1177/1060028013509792. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Ann Pharmacother. 2013. PMID: 24259629 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Biomarkers for Acute Myocardial Infarction Based on Cell Senescence Genes and Machine Learning.Anatol J Cardiol. 2025 Aug;29(8):409-422. doi: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2025.5129. Anatol J Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40771115 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Clinical Cardiotoxicity Incidence of FDA-Approved Small-Molecule Kinase Inhibitors.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jun 12;11:891. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00891. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32595510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Regorafenib-A Multikinase Inhibitor in Pulmonary Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 2;22(3):1502. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031502. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33540939 Free PMC article.
-
A Rare Case of Regorafenib-Induced ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction.Cureus. 2023 May 31;15(5):e39779. doi: 10.7759/cureus.39779. eCollection 2023 May. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37398771 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilhelm SM, Dumas J, Adnane L, et al. Regorafenib (BAY 73-4506): a new oral multikinase inhibitor of angiogenic, stromal and oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinases with potent preclinical antitumor activity. Int J Cancer. 2011;129(1):245–255. - PubMed
-
- Grothey A, Van Cutsem E, Sobrero A, et al. Regorafenib monotherapy for previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (CORRECT): an international, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2013;381(9863):303–312. - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Rahman O, Fouad M. Risk of cardiovascular toxicities in patients with solid tumors treated with sunitinib, axitinib, cediranib or regorafenib: an updated systematic review and comparative meta-analysis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2014;92(3):194–207. - PubMed
-
- Wang Z, Xu J, Nie W, et al. Risk of hypertension with regorafenib in cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;70(2):225–231. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
