Myelin-specific Th17 cells induce severe relapsing optic neuritis with irreversible loss of retinal ganglion cells in C57BL/6 mice
- PMID: 27122964
- PMCID: PMC4830397
Myelin-specific Th17 cells induce severe relapsing optic neuritis with irreversible loss of retinal ganglion cells in C57BL/6 mice
Abstract
Purpose: Optic neuritis affects most patients with multiple sclerosis (MS), and current treatments are unreliable. The purpose of this study was to characterize the contribution of Th1 and Th17 cells to the development of optic neuritis.
Methods: Mice were passively transferred myelin-specific Th1 or Th17 cells to induce experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a model of neuroautoimmunity. Visual acuity was assessed daily with optokinetic tracking, and 1, 2, and 3 weeks post-induction, optic nerves and retinas were harvested for immunohistochemical analyses.
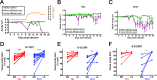
Results: Passive transfer experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis elicits acute episodes of asymmetric visual deficits and is exacerbated in Th17-EAE relative to Th1-EAE. The Th17-EAE optic nerves contained more inflammatory infiltrates and an increased neutrophil to macrophage ratio. Significant geographic degeneration of the retinal ganglion cells accompanied Th17-EAE but not Th1.
Conclusions: Th17-induced transfer EAE recapitulates pathologies observed in MS-associated optic neuritis, namely, monocular episodes of vision loss, optic nerve inflammation, and geographic retinal ganglion cell (RGC) degeneration.
Figures





References
-
- Pinholt M, Frederiksen JL, Andersen PS, Christiansen M. Apo E in multiple sclerosis and optic neuritis: the apo E-epsilon4 allele is associated with progression of multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. 2005;11:511–5. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&lis... - PubMed
-
- Kaur P, Bennett JL. Optic neuritis and the neuro-ophthalmology of multiple sclerosis. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2007;79:633–63. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&lis... - PubMed
-
- Beck RW, Cleary PA, Backlund JC. The course of visual recovery after optic neuritis. Experience of the Optic Neuritis Treatment Trial. Ophthalmology. 1994;101:1771–8. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&lis... - PubMed
-
- Fjeldstad C, Bemben M, Pardo G. Reduced retinal nerve fiber layer and macular thickness in patients with multiple sclerosis with no history of optic neuritis identified by the use of spectral domain high-definition optical coherence tomography. J Clin Neurosci. 2011;18:1469–72. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&lis... - PubMed
-
- Brusaferri F, Candelise L. Steroids for multiple sclerosis and optic neuritis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. J Neurol. 2000;247:435–42. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&lis... - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

