Electroacupuncture Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury in Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion of Rat via Modulation of Apoptosis, Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Excitotoxicity
- PMID: 27123035
- PMCID: PMC4830716
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/9438650
Electroacupuncture Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury in Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion of Rat via Modulation of Apoptosis, Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Excitotoxicity
Abstract
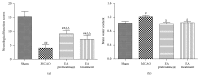
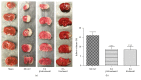
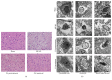
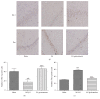
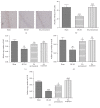
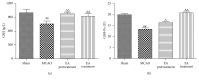
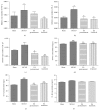
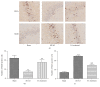
Electroacupuncture (EA) has several properties such as antioxidant, antiapoptosis, and anti-inflammatory properties. The current study was to investigate the effects of EA on the prevention and treatment of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury and to elucidate possible molecular mechanisms. Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) for 2 h followed by reperfusion for 24 h. EA stimulation was applied to both Baihui and Dazhui acupoints for 30 min in each rat per day for 5 successive days before MCAO (pretreatment) or when the reperfusion was initiated (treatment). Neurologic deficit scores, infarction volumes, brain water content, and neuronal apoptosis were evaluated. The expressions of related inflammatory cytokines, apoptotic molecules, antioxidant systems, and excitotoxic receptors in the brain were also investigated. Results showed that both EA pretreatment and treatment significantly reduced infarct volumes, decreased brain water content, and alleviated neuronal injury in MCAO rats. Notably, EA exerts neuroprotection against I/R injury through improving neurological function, attenuating the inflammation cytokines, upregulating antioxidant systems, and reducing the excitotoxicity. This study provides a better understanding of the molecular mechanism underlying the traditional use of EA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Electroacupuncture Pretreatment Elicits Neuroprotection Against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats Associated with Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1-Mediated Anti-Oxidant Stress and Anti-Inflammation.Inflammation. 2019 Oct;42(5):1777-1787. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-01040-y. Inflammation. 2019. PMID: 31190106
-
Electroacupuncture-like stimulation at the Baihui (GV20) and Dazhui (GV14) acupoints protects rats against subacute-phase cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injuries by reducing S100B-mediated neurotoxicity.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 13;9(3):e91426. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091426. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24626220 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture-like stimulation at Baihui and Dazhui acupoints exerts neuroprotective effects through activation of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor-mediated MEK1/2/ERK1/2/p90RSK/bad signaling pathway in mild transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Mar 7;14:92. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-92. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 24606810 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture Pretreatment Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats Through Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1-Mediated Anti-apoptosis via Inhibiting NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Neuroscience. 2022 Feb 1;482:100-115. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2021.12.017. Epub 2021 Dec 17. Neuroscience. 2022. PMID: 34929338
-
Electroacupuncture Pretreatment as a Novel Avenue to Protect Heart against Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 May 18;2020:9786482. doi: 10.1155/2020/9786482. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32508960 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Electroacupuncture ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing autophagy via the SIRT1-FOXO1 signaling pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Jul 3;12(13):13187-13205. doi: 10.18632/aging.103420. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32620714 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture Pretreatment Elicits Neuroprotection Against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats Associated with Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1-Mediated Anti-Oxidant Stress and Anti-Inflammation.Inflammation. 2019 Oct;42(5):1777-1787. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-01040-y. Inflammation. 2019. PMID: 31190106
-
Electroacupuncture Promotes the Survival of the Grafted Human MGE Neural Progenitors in Rats with Cerebral Ischemia by Promoting Angiogenesis and Inhibiting Inflammation.Neural Plast. 2021 Oct 7;2021:4894881. doi: 10.1155/2021/4894881. eCollection 2021. Neural Plast. 2021. PMID: 34659396 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture and neuroregeneration in ischemic stroke.Neural Regen Res. 2018 Apr;13(4):573-583. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.230272. Neural Regen Res. 2018. PMID: 29722298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ezetimibe Attenuates Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation via the AMPK/Nrf2/TXNIP Pathway after MCAO in Rats.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Jan 4;2020:4717258. doi: 10.1155/2020/4717258. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 31998437 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

