N-glycosylation of R-spondin1 at Asn137 negatively regulates its secretion and Wnt/β-catenin signaling-enhancing activity
- PMID: 27123103
- PMCID: PMC4841080
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2016.4425
N-glycosylation of R-spondin1 at Asn137 negatively regulates its secretion and Wnt/β-catenin signaling-enhancing activity
Abstract
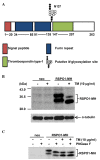
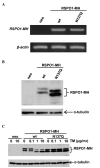
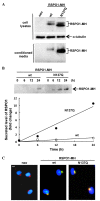
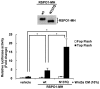
N-glycosylation is a post-translational protein modification with a wide variety of functions. It has been predicted that R-spondin1 (RSPO1) is N-glycosylated, although this remains unknown. The present study identified that RSPO1 was N-glycosylated at Asn137, and that N-glycosylation of RSPO1 negatively influenced its secretion and enhancing effect on Wnt/β-catenin signaling. In vitro treatment with peptide-N-glycosidase F increased the electrophoretic mobility of RSPO1. Furthermore, treatment of wild-type (wt) RSPO1-overexpressing HT1080 cells with tunicamycin (TM), which inhibits N-glycosylation, resulted in a significant reduction in the molecular weight of RSPO1. However, TM treatment had no effect in the RSPO1 mutant whereby the Asn137 residue was replaced by Gln (N137Q). These results demonstrated for the first time that RSPO1 is N-glycosylated at Asn137. RSPO1 is a secreted protein that has Wnt/β-catenin signaling-enhancing activity and is expected to have therapeutic applications. The role of N-glycosylation in RSPO1 was evaluated by conducting comparative experiments with wt and N137Q RSPO1, which revealed that the N137Q mutant increased the secretion and Wnt/β-catenin signaling-enhancing effect of RSPO1, compared with wt RSPO1. These results suggest that N-glycosylation of RSPO1 has a negative influence on its secretion and Wnt/β-catenin signaling-enhancing effect.
Keywords: N-linked glycosylation; R-spondin1; Wnt signaling; glycosylation; heparin-binding protein; protein secretion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of DPY19L3 as the C-mannosyltransferase of R-spondin1 in human cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Mar 1;27(5):744-56. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-06-0373. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 26764097 Free PMC article.
-
N-Glycosylation of Human R-Spondin 1 Is Required for Efficient Secretion and Stability but Not for Its Heparin Binding Ability.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jun 14;17(6):937. doi: 10.3390/ijms17060937. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27314333 Free PMC article.
-
R-Spondin1 protects mice from chemotherapy or radiation-induced oral mucositis through the canonical Wnt/beta-catenin pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Feb 17;106(7):2331-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0805159106. Epub 2009 Jan 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19179402 Free PMC article.
-
R-spondin1, WNT4, and the CTNNB1 signaling pathway: strict control over ovarian differentiation.Reproduction. 2014 Dec;148(6):R97-110. doi: 10.1530/REP-14-0177. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Reproduction. 2014. PMID: 25187620 Review.
-
Tipping the balance: modulating the Wnt pathway for tissue repair.Trends Biotechnol. 2009 Mar;27(3):131-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2008.11.007. Epub 2009 Jan 31. Trends Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19187992 Review.
Cited by
-
Production, purification and characterization of recombinant human R-spondin1 (RSPO1) protein stably expressed in human HEK293 cells.BMC Biotechnol. 2020 Jan 20;20(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12896-020-0600-0. BMC Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31959207 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of DPY19L3 as the C-mannosyltransferase of R-spondin1 in human cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Mar 1;27(5):744-56. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-06-0373. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 26764097 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
