Differential diagnostic value of computed tomography perfusion combined with vascular endothelial growth factor expression in head and neck lesions
- PMID: 27123114
- PMCID: PMC4840932
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2016.4413
Differential diagnostic value of computed tomography perfusion combined with vascular endothelial growth factor expression in head and neck lesions
Abstract
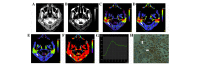
There are numerous types of head and neck lesions (HNLs), and conventional computed tomography (CT) has low specificity and sensitivity in the definitive and differential diagnosis of HNLs. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the value of perfusion CT (CTP) combined with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in the differentiation between malignant and benign HNLs. In total, 41 HNLs, which were pathologically confirmed, underwent CTP and VEGF expression analysis. All lesions were divided into three groups: Group A, benign hypovascular lesions; Group B, benign hypervascular lesions; and Group C, malignant lesions. Time density curve (TDC) and CTP parameters [maximum intensity projection (MIP), blood volume (BV), blood flow (BF), mean transit time and capillary permeability] were analyzed. The association between perfusion measurements and VEGF was assessed using Pearson's correlation. TDCs were classified into three types, and type I was more frequently identified in benign tumors (Groups A and B) compared with malignant tumors (Group C) (P=0.003). Malignant tumors primarily had a TDC of type II and III. MIP, BF and BV were all significantly higher in Groups B and C compared to Group A (P<0.01). VEGF expression of malignant tumors was significantly higher than benign tumors (P=0.007). No correlation was identified between VEGF and any CTP parameter. The present findings suggest that CTP combined with VEGF may differentiate between malignant and benign HNLs, and between benign hypovascular and hypervascular lesions.
Keywords: angiogenesis; computed tomography; head and neck lesions; perfusion; vascular endothelial growth factor.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Perfusion Computed Tomography Scan Imaging in Differentiation of Benign from Malignant Parotid Lesions.Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Apr;24(2):e160-e169. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1697005. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020. PMID: 32256836 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary lesions: correlative study of dynamic triple-phase enhanced CT perfusion imaging with tumor angiogenesis and vascular endothelial growth factor expression.BMC Med Imaging. 2021 Oct 30;21(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s12880-021-00692-3. BMC Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34717573 Free PMC article.
-
Squamous cell cancer of hypopharynx and larynx - evaluation of metastatic nodal disease based on computed tomography perfusion studies.Eur J Radiol. 2012 May;81(5):1034-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2011.01.084. Epub 2011 Feb 16. Eur J Radiol. 2012. PMID: 21324623
-
Quantification of angiogenesis by functional computed tomography in a Matrigel model in rats.Acad Radiol. 2004 May;11(5):573-82. doi: 10.1016/S1076-6332(03)00728-1. Acad Radiol. 2004. PMID: 15147622
-
Diagnostic Performance of Perfusion Computed Tomography for Differentiating Lung Cancer from Benign Lesions: A Meta-Analysis.Med Sci Monit. 2019 May 11;25:3485-3494. doi: 10.12659/MSM.914206. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31077263 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic value of one-stop CT energy spectrum and perfusion for angiogenesis in colon and rectum cancer.BMC Med Imaging. 2024 May 21;24(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01291-8. BMC Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38773384 Free PMC article.
-
Perfusion Computed Tomography Scan Imaging in Differentiation of Benign from Malignant Parotid Lesions.Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Apr;24(2):e160-e169. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1697005. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020. PMID: 32256836 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic contrast-enhanced computed tomography in dogs with nasal tumors.J Vet Intern Med. 2023 May-Jun;37(3):1146-1154. doi: 10.1111/jvim.16722. Epub 2023 Apr 24. J Vet Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 37092693 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of preoperative CT enhancement rate and CT perfusion parameters in colorectal cancer.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 May 21;24(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03257-0. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38773485 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee TY, Purdie TG, Stewart E. CT imaging of angiogenesis. Q J Nucl Med. 2003;47:171–187. - PubMed
-
- Li C, Fan J, Song X, Zhang B, Chen Y, Li C, Mi K, Ma H, Song Y, Tao X, Li G. Expression of angiopoietin-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 correlates with lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis and affects survival of oral squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 2013;8:e75388. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0075388. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Oliveira MV, Pereira Gomes EP, Pereira CS, de Souza LR, Barros LO, Mendes DC, Guimarães AL, De Paula AM. Prognostic value of microvessel density and p53 expression on the locoregional metastasis and survival of the patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2013;21:444–451. doi: 10.1097/PAI.0b013e3182773125. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
