Deleterious mutation in GPR88 is associated with chorea, speech delay, and learning disabilities
- PMID: 27123486
- PMCID: PMC4830197
- DOI: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000064
Deleterious mutation in GPR88 is associated with chorea, speech delay, and learning disabilities
Abstract
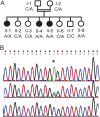
Objective: To identify the underlying molecular basis of a familial developmental disorder characterized by chorea, marked speech delay, and learning difficulties in 4 sisters from a consanguineous family.
Methods: Whole-exome analysis of DNA of the 2 older patients followed by Sanger sequencing of the mutated exon in all family members.
Results: A homozygous deleterious mutation, p.C291X, was identified in the GPR88 gene in both exome analyses. The mutation segregated with the disease in the family and was absent from a large cohort of controls.
Conclusions: Homozygous deleterious mutation in GPR88 in humans is associated with marked speech delay, learning disabilities, and chorea, which manifest at 8-9 years of age. The finding is consistent with the reported abundant expression of GPR88 in the striatum and the hyperkinetic activity and learning impairment observed in GPR88 knockout mice. Although further functional characterization is needed, the finding underscores the importance of GPR88 in movement control and learning.
Figures
References
-
- Hermann A, Walker RH. Diagnosis and treatment of chorea syndromes. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2015;15:514–525. - PubMed
-
- Breedveld GJ, van Dongen JWF, Danesino C, et al. Mutations in TITF-1 are associated with benign hereditary chorea. Hum Mol Genet 2002;11:971–979. - PubMed
-
- DeLong MR. Primate models of movement disorders of basal ganglia origin. Trends Neurosci 1990;13:281–285. - PubMed
-
- Massart R, Guilloux JP, Mignon V, et al. Striatal GPR88 expression is confined to the whole projection neuron population and is regulated by dopaminergic and glutamatergic afferents. Eur J Neurosci 2009;30:397–414. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
