Exploratory Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Response-Guided Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Hormone Positive Breast Cancer Patients
- PMID: 27124410
- PMCID: PMC4849576
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154386
Exploratory Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Response-Guided Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Hormone Positive Breast Cancer Patients
Abstract
Purpose: Guiding response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (guided-NACT) allows for an adaptative treatment approach likely to improve breast cancer survival. In this study, our primary aim is to explore the expected cost-effectiveness of guided-NACT using as a case study the first randomized controlled trial that demonstrated effectiveness (GeparTrio trial).
Materials and methods: As effectiveness was shown in hormone-receptor positive (HR+) early breast cancers (EBC), our decision model compared the health-economic outcomes of treating a cohort of such women with guided-NACT to conventional-NACT using clinical input data from the GeparTrio trial. The expected cost-effectiveness and the uncertainty around this estimate were estimated via probabilistic cost-effectiveness analysis (CEA), from a Dutch societal perspective over a 5-year time-horizon.
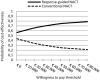
Results: Our exploratory CEA predicted that guided-NACT as proposed by the GeparTrio, costs additional €110, but results in 0.014 QALYs gained per patient. This scenario of guided-NACT was considered cost-effective at any willingness to pay per additional QALY. At the prevailing Dutch willingness to pay threshold (€80.000/QALY) cost-effectiveness was expected with 78% certainty.
Conclusion: This exploratory CEA indicated that guided-NACT (as proposed by the GeparTrio trial) is likely cost-effective in treating HR+ EBC women. While prospective validation of the GeparTrio findings is advisable from a clinical perspective, early CEAs can be used to prioritize further research from a broader health economic perspective, by identifying which parameters contribute most to current decision uncertainty. Furthermore, their use can be extended to explore the expected cost-effectiveness of alternative guided-NACT scenarios that combine the use of promising imaging techniques together with personalized treatments.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness and resource use of implementing MRI-guided NACT in ER-positive/HER2-negative breast cancers in The Netherlands.BMC Cancer. 2016 Sep 5;16(1):712. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2653-y. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27595620 Free PMC article.
-
Economic Analysis of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Versus Primary Debulking Surgery for Advanced Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Using an Aggressive Surgical Paradigm.Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2018 Jul;28(6):1077-1084. doi: 10.1097/IGC.0000000000001271. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29683880 Free PMC article.
-
Cost effectiveness of neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by interval cytoreductive surgery versus primary cytoreductive surgery for patients with advanced stage ovarian cancer during the initial treatment phase.Gynecol Oncol. 2018 Feb;148(2):329-335. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2017.12.015. Epub 2017 Dec 19. Gynecol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29273308 Free PMC article.
-
Economic evaluation of docetaxel for breast cancer.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2009 Feb;10(2):283-90. doi: 10.1517/14656560802653206. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2009. PMID: 19236199 Review.
-
Cost effectiveness of treatment options in advanced breast cancer in the UK.Pharmacoeconomics. 2001;19(11):1091-102. doi: 10.2165/00019053-200119110-00003. Pharmacoeconomics. 2001. PMID: 11735676 Review.
Cited by
-
Cost-effectiveness of monitoring endoxifen levels in breast cancer patients adjuvantly treated with tamoxifen.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018 Nov;172(1):143-150. doi: 10.1007/s10549-018-4886-8. Epub 2018 Jul 13. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018. PMID: 30006796 Free PMC article.
-
How is overall survival assessed in randomised clinical trials in cancer and are subsequent treatment lines considered? A systematic review.Trials. 2023 Nov 6;24(1):708. doi: 10.1186/s13063-023-07730-1. Trials. 2023. PMID: 37926806 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of adding atezolizumab to first-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced triple-negative breast cancer.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020 May 5;12:1758835920916000. doi: 10.1177/1758835920916000. eCollection 2020. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32426048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fisher B, Bryant J, Wolmark N, Mamounas E, Brown A, Fisher ER, et al. Effect of preoperative chemotherapy on the outcome of women with operable breast cancer. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 1998;16: 2672–2685. - PubMed
-
- van der Hage JA, van de Velde CJ, Julien JP, Tubiana-Hulin M, Vandervelden C, Duchateau L. Preoperative chemotherapy in primary operable breast cancer: results from the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer trial 10902. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2001;19: 4224–4237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

