Serum Levels of TNF Receptor Ligands Are Dysregulated in Sepsis and Predict Mortality in Critically Ill Patients
- PMID: 27124414
- PMCID: PMC4849634
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153765
Serum Levels of TNF Receptor Ligands Are Dysregulated in Sepsis and Predict Mortality in Critically Ill Patients
Abstract
Introduction: TNF superfamily members, including TNF-related weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) and Glucocorticoid-Induced TNFR-Related Protein Ligand (GITRL) have been described as serum based biomarkers for inflammatory and immune mediated diseases. However, up to now the role of TWEAK and GITRL has not been analyzed in critical illness and sepsis.
Methods: GITRL and TWEAK serum concentrations were measured in 121 critically ill patients (84 fulfilled with septic disease), in comparison to 50 healthy controls. Results were correlated with clinical data.
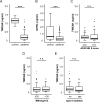
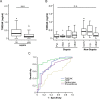
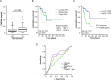
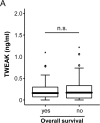
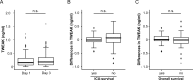
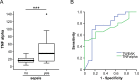
Results: Serum levels of TWEAK and GITRL were strongly decreased in critically ill patients compared with healthy controls. Concentrations of TWEAK (but not GITRL) were further decreased in patients with sepsis and correlated with routinely used markers of inflammation and bacterial infection such as C-reactive protein, procalcitonin and Interleukin-6. Notably, we failed to detect a correlation to other TNFR ligands such as TNF or APRIL. Finally, TWEAK levels of the upper quartile of the cohort were prognostic for mortality during ICU treatment.
Conclusion: TWEAK and GITRL levels were lower in intensive care unit medical patients. Levels of TWEAK were further decreased in septic patients, and alterations in TWEAK concentrations were linked to an unfavorable outcome. Together with recently published results on other TNFR ligands, these data indicate specific functions of the different TNFR ligands in septic diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum concentrations of A Proliferation-Inducing Ligand (APRIL) are elevated in sepsis and predict mortality in critically ill patients.J Crit Care. 2013 Oct;28(5):882.e1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2012.11.007. Epub 2013 Jan 20. J Crit Care. 2013. PMID: 23337484
-
Serum TNF-related and weak inducer of apoptosis levels in septic shock patients.Ther Apher Dial. 2011 Aug;15(4):342-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-9987.2011.00966.x. Ther Apher Dial. 2011. PMID: 21884467
-
Elevated asymmetric dimethylarginine levels predict short- and long-term mortality risk in critically ill patients.J Crit Care. 2013 Dec;28(6):947-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2013.05.016. Epub 2013 Aug 14. J Crit Care. 2013. PMID: 23953490
-
The efficacy of procalcitonin as a biomarker in the management of sepsis: slaying dragons or tilting at windmills?Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2013 Dec;14(6):489-511. doi: 10.1089/sur.2012.028. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2013. PMID: 24274059 Review.
-
Interpretation of C-reactive protein concentrations in critically ill patients.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:124021. doi: 10.1155/2013/124021. Epub 2013 Oct 28. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24286072 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential Roles of Tumor Necrosis Factor Ligand Superfamily Members as Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer.J Clin Med. 2018 Jul 13;7(7):175. doi: 10.3390/jcm7070175. J Clin Med. 2018. PMID: 30011858 Free PMC article.
-
Weaning Failure in Critically Ill Patients Is Related to the Persistence of Sepsis Inflammation.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Dec 31;12(1):92. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12010092. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35054259 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of TNF-α genetic polymorphisms as predictors for sepsis susceptibility and progression.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 14;20(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-4910-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32171247 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating cell death biomarker TRAIL is associated with increased organ dysfunction in sepsis.JCI Insight. 2019 May 2;4(9):e127143. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.127143. eCollection 2019 May 2. JCI Insight. 2019. PMID: 31045578 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated Serum Levels of Mixed Lineage Kinase Domain-Like Protein Predict Survival of Patients during Intensive Care Unit Treatment.Dis Markers. 2018 Feb 11;2018:1983421. doi: 10.1155/2018/1983421. eCollection 2018. Dis Markers. 2018. PMID: 29606984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peschon JJ, Slack JL, Reddy P, Stocking KL, Sunnarborg SW, Lee DC, et al. An essential role for ectodomain shedding in mammalian development. Science. 1998; 282(5392):1281–4. . - PubMed
-
- De Freitas I, Fernandez-Somoza M, Essenfeld-Sekler E, Cardier JE. Serum levels of the apoptosis-associated molecules, tumor necrosis factor-alpha/tumor necrosis factor type-I receptor and Fas/FasL, in sepsis. Chest. 2004; 125(6):2238–46. . - PubMed
-
- Chicheportiche Y, Bourdon PR, Xu H, Hsu YM, Scott H, Hession C, et al. TWEAK, a new secreted ligand in the tumor necrosis factor family that weakly induces apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1997; 272(51):32401–10. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

