Localization of RNAPII and 3' end formation factor CstF subunits on C. elegans genes and operons
- PMID: 27124504
- PMCID: PMC4984680
- DOI: 10.1080/21541264.2016.1168509
Localization of RNAPII and 3' end formation factor CstF subunits on C. elegans genes and operons
Abstract
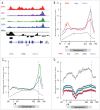
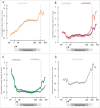
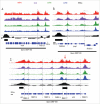
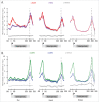
Transcription termination is mechanistically coupled to pre-mRNA 3' end formation to prevent transcription much beyond the gene 3' end. C. elegans, however, engages in polycistronic transcription of operons in which 3' end formation between genes is not accompanied by termination. We have performed RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) and CstF ChIP-seq experiments to investigate at a genome-wide level how RNAPII can transcribe through multiple poly-A signals without causing termination. Our data shows that transcription proceeds in some ways as if operons were composed of multiple adjacent single genes. Total RNAPII shows a small peak at the promoter of the gene cluster and a much larger peak at 3' ends. These 3' peaks coincide with maximal phosphorylation of Ser2 within the C-terminal domain (CTD) of RNAPII and maximal localization of the 3' end formation factor CstF. This pattern occurs at all 3' ends including those at internal sites in operons where termination does not occur. Thus the normal mechanism of 3' end formation does not always result in transcription termination. Furthermore, reduction of CstF50 by RNAi did not substantially alter the pattern of CstF64, total RNAPII, or Ser2 phosphorylation at either internal or terminal 3' ends. However, CstF50 RNAi did result in a subtle reduction of CstF64 binding upstream of the site of 3' cleavage, suggesting that the CstF50/CTD interaction may facilitate bringing the 3' end machinery to the transcription complex.
Keywords: CTD phosphorylation; RNA Polymerase II; RNAPII termination; Transcription; cleavage stimulatory factor; torpedo model.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain phosphorylation patterns in Caenorhabditis elegans operons, polycistronic gene clusters with only one promoter.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Aug;30(15):3887-93. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00325-10. Epub 2010 May 24. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20498277 Free PMC article.
-
Genes involved in pre-mRNA 3'-end formation and transcription termination revealed by a lin-15 operon Muv suppressor screen.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Oct 28;105(43):16665-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0807104105. Epub 2008 Oct 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18946043 Free PMC article.
-
Two distinct transcription termination modes dictated by promoters.Genes Dev. 2017 Sep 15;31(18):1870-1879. doi: 10.1101/gad.301093.117. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Genes Dev. 2017. PMID: 29021241 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic phosphorylation patterns of RNA polymerase II CTD during transcription.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1829(1):55-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.08.013. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22982363 Review.
-
Operon and non-operon gene clusters in the C. elegans genome.WormBook. 2015 Apr 28:1-20. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.175.1. WormBook. 2015. PMID: 25936768 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RNA polymerase II CTD S2P is dispensable for embryogenesis but mediates exit from developmental diapause in C. elegans.Sci Adv. 2020 Dec 9;6(50):eabc1450. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abc1450. Print 2020 Dec. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 33298437 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstitution of the CstF complex unveils a regulatory role for CstF-50 in recognition of 3'-end processing signals.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 25;46(2):493-503. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1177. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29186539 Free PMC article.
-
hnRNPL-CstF64 complex: coordinating CSR and LSR in IgH locus recombination dynamics through eRNA and NHEJ regulation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Aug 27;53(16):gkaf810. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf810. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40902003 Free PMC article.
-
CFIm25 regulates human stem cell function independently of its role in mRNA alternative polyadenylation.RNA Biol. 2022;19(1):686-702. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2022.2071025. Epub 2021 Dec 31. RNA Biol. 2022. PMID: 35491945 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue-Specific Transcription Footprinting Using RNA PoI DamID (RAPID) in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2020 Dec;216(4):931-945. doi: 10.1534/genetics.120.303774. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Genetics. 2020. PMID: 33037050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- West S, Gromak N, Proudfoot NJ. Human 5′ –>3′ exonuclease Xrn2 promotes transcription termination at co-transcriptional cleavage sites. Nature 2004; 432(7016):522-525. - PubMed
-
- Kim M, Krogan NJ, Vasiljeva L, Rando OJ, Nedea E, Greenblatt JF, Buratowski S. The yeast Rat1 exonuclease promotes transcription termination by RNA polymerase II. Nature 2004; 432(7016):517-522. - PubMed
-
- Srivastava R, Ahn SH. Modifications of RNA polymerase II CTD: Connections to the histone code and cellular function. Biotechnol Adv 2015; 33(6 Pt 1):856-872. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
