Germline loss of PKM2 promotes metabolic distress and hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 27125672
- PMCID: PMC4863734
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.278549.116
Germline loss of PKM2 promotes metabolic distress and hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
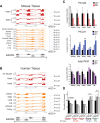
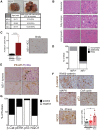
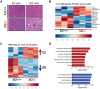
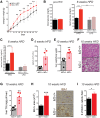
Alternative splicing of the Pkm gene product generates the PKM1 and PKM2 isoforms of pyruvate kinase (PK), and PKM2 expression is closely linked to embryogenesis, tissue regeneration, and cancer. To interrogate the functional requirement for PKM2 during development and tissue homeostasis, we generated germline PKM2-null mice (Pkm2(-/-)). Unexpectedly, despite being the primary isoform expressed in most wild-type adult tissues, we found that Pkm2(-/-) mice are viable and fertile. Thus, PKM2 is not required for embryonic or postnatal development. Loss of PKM2 leads to compensatory expression of PKM1 in the tissues that normally express PKM2. Strikingly, PKM2 loss leads to spontaneous development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with high penetrance that is accompanied by progressive changes in systemic metabolism characterized by altered systemic glucose homeostasis, inflammation, and hepatic steatosis. Therefore, in addition to its role in cancer metabolism, PKM2 plays a role in controlling systemic metabolic homeostasis and inflammation, thereby preventing HCC by a non-cell-autonomous mechanism.
Keywords: HCC; PKM2; metabolism.
© 2016 Dayton et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

References
-
- Baffy G, Brunt EM, Caldwell SH. 2012. Hepatocellular carcinoma in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: an emerging menace. J Hepatol 56: 1384–1391. - PubMed
-
- Barros RPA, Gustafsson J-Å. 2011. Estrogen receptors and the metabolic network. Cell Metab 14: 289–299. - PubMed
-
- Byrne CD, Targher G. 2015. NAFLD: a multisystem disease. J Hepatol 62: S47–S64. - PubMed
-
- Cairns RA, Harris IS, Mak TW. 2011. Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer 11: 85–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
