Retinal glial responses to optic nerve crush are attenuated in Bax-deficient mice and modulated by purinergic signaling pathways
- PMID: 27126275
- PMCID: PMC4850653
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-016-0558-y
Retinal glial responses to optic nerve crush are attenuated in Bax-deficient mice and modulated by purinergic signaling pathways
Abstract
Background: Retinal ganglion cell (RGC) soma death is a consequence of optic nerve damage, including in optic neuropathies like glaucoma. The activation of the innate immune network in the retina after nerve damage has been linked to RGC pathology. Since the eye is immune privileged, innate immune functions are the responsibility of the glia, specifically the microglia, astrocytes, and Müller cells that populate the retina. Glial activation, leading to the production of inflammatory cytokines, is a hallmark feature of retinal injury resulting from optic nerve damage and purported to elicit secondary degeneration of RGC somas.
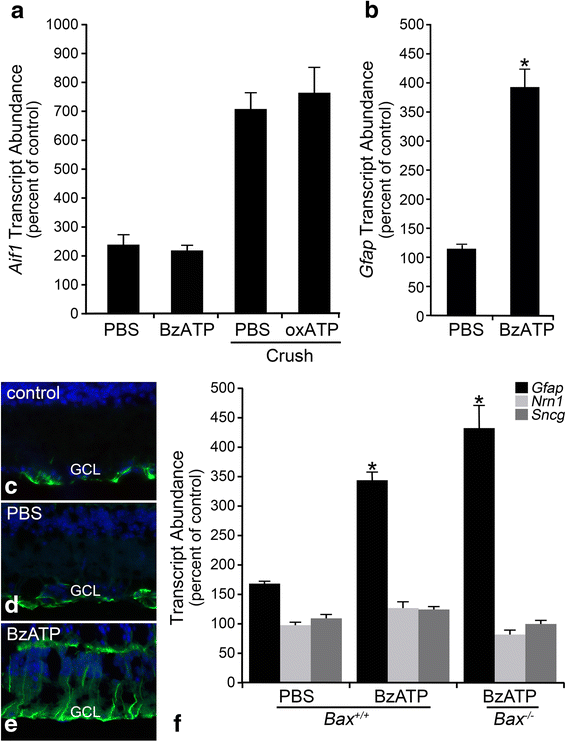
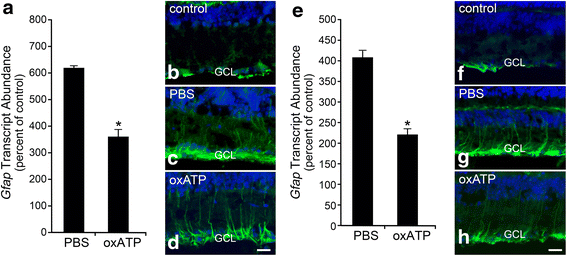
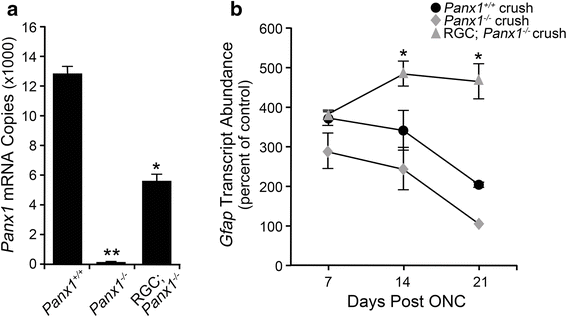
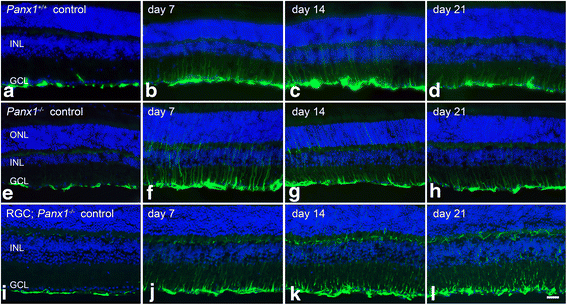
Methods: A mouse model of optic nerve crush (ONC) was used to study retinal glial activation responses. RGC apoptosis was blocked using Bax-deficient mice. Glial activation responses were monitored by quantitative PCR and immunofluorescent labeling in retinal sections of activation markers. ATP signaling pathways were interrogated using P2X receptor agonists and antagonists and Pannexin 1 (Panx1)-deficient mice with RGC-specific deletion.
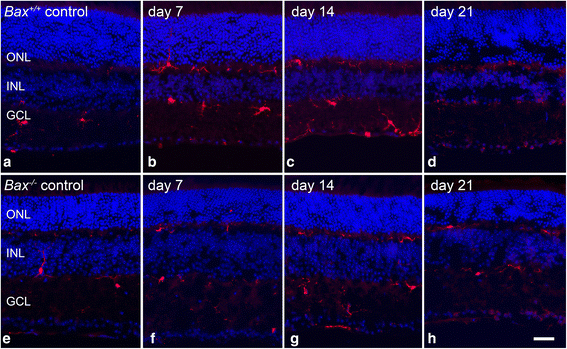
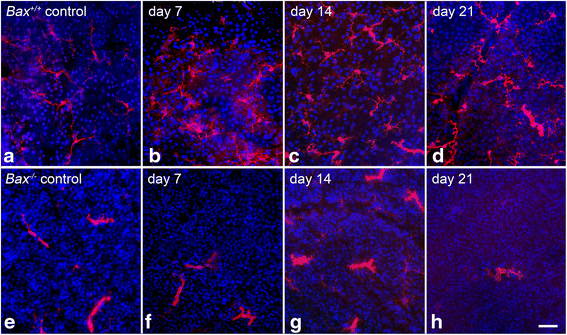
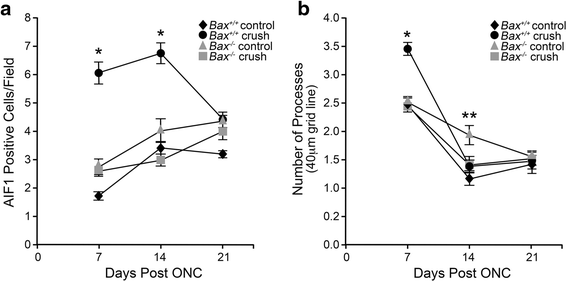
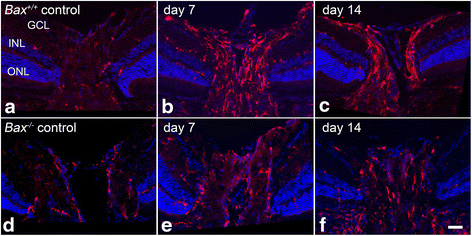
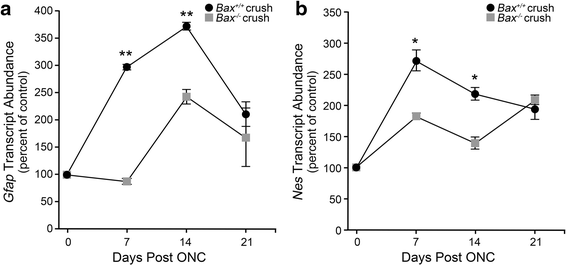
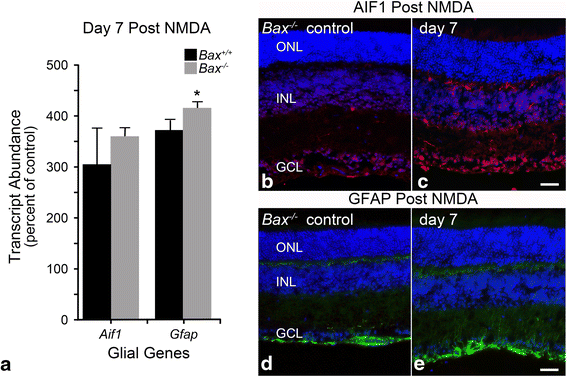
Results: ONC induced activation of both macroglia and microglia in the retina, and both these responses were dramatically muted if RGC death was blocked by deletion of the Bax gene. Macroglial, but not microglial, activation was modulated by purinergic receptor activation. Release of ATP after optic nerve damage was not mediated by PANX1 channels in RGCs.
Conclusions: RGC death in response to ONC plays a principal stimulatory role in the retinal glial activation response.
Keywords: BAX; Macroglia; Microglia; Neuroinflammation; Optic nerve damage; P2X Receptor; PANX1; Retinal ganglion cell.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha has an early protective effect on retinal ganglion cells after optic nerve crush.J Neuroinflammation. 2014 Nov 19;11:194. doi: 10.1186/s12974-014-0194-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2014. PMID: 25407441 Free PMC article.
-
BAX-Depleted Retinal Ganglion Cells Survive and Become Quiescent Following Optic Nerve Damage.Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Feb;57(2):1070-1084. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01783-7. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 31673950 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor-4 knockout mice are more resistant to optic nerve crush damage than wild-type mice.Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2015 Sep-Oct;43(7):655-65. doi: 10.1111/ceo.12521. Epub 2015 May 13. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 25752496
-
Neuroinflammation, Microglia and Implications for Retinal Ganglion Cell Survival and Axon Regeneration in Traumatic Optic Neuropathy.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 4;13:860070. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.860070. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35309305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Inhibition of stress-responsive signaling pathway prevents neural cell death following optic nerve injury].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2014 Nov;118(11):907-15. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2014. PMID: 25543382 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Molecular regulation of neuroinflammation in glaucoma: Current knowledge and the ongoing search for new treatment targets.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2022 Mar;87:100998. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2021.100998. Epub 2021 Aug 1. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 34348167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retinal ganglion cell survival after severe optic nerve injury is modulated by crosstalk between Jak/Stat signaling and innate immune responses in the zebrafish retina.Development. 2022 Apr 15;149(8):dev199694. doi: 10.1242/dev.199694. Epub 2021 Oct 26. Development. 2022. PMID: 34528064 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the Immune System for the Treatment of Glaucoma.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018;16(7):942-958. doi: 10.2174/1570159X15666170720094529. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28730968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Facile Strategy to Restore the Optic Nerve Functionality Using an Injectable Conducting Hydrogel.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jun;12(21):e2415601. doi: 10.1002/advs.202415601. Epub 2025 Apr 17. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40245175 Free PMC article.
-
Ozone: a natural bioactive molecule with antioxidant property as potential new strategy in aging and in neurodegenerative disorders.Ageing Res Rev. 2020 Nov;63:101138. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101138. Epub 2020 Aug 15. Ageing Res Rev. 2020. PMID: 32810649 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tezel G, Li LY, Patil RV, Wax MB. TNF-alpha and TNF-alpha receptor-1 in the retina of normal and glaucomatous eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001;42:1787–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

