Rigenera protocol in the treatment of surgical wound dehiscence
- PMID: 27126653
- PMCID: PMC7949493
- DOI: 10.1111/iwj.12601
Rigenera protocol in the treatment of surgical wound dehiscence
Abstract
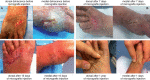
The effective management of post-operative wounds is important to prevent potential complications such as surgical-site infections and wound dehiscence. The purpose of this study was to treat wound dehiscence in elderly patients who were subjected to orthopaedic surgical interventions. The dehisced wounds were treated with autologous micro-grafts obtained using a promising CE-certified medical device called Rigeneracons. This instrument is a biological disruptor of human tissues able to specifically select progenitor cells that, as already reported in previous studies, maintain high cell viability but mainly have a high regenerative potential, allowing the repair of damaged tissues. Autologous micro-grafts obtained by Rigeneracons are ready to use and can be applied alone or in combination with biological scaffolds directly on the injured area. We observed in our patients a complete remission of dehisced wounds, on average, after 30 days from micro-grafts application and a total wound re-epithelialisation after 1 year from the surgical intervention. In conclusion, although we reported only three patients, autologous micro-grafts can be considered a promising approach for the treatment of dehisced wounds, improving the wound-healing process and in general the patient's quality of life without using other dressings.
Keywords: Autologous; Dehiscence; Micro-grafts; Tissue regeneration; Wound healing.
© 2016 Medicalhelplines.com Inc and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Yao K, Bae L, Yew WP. Post‐operative wound management. Aust Fam Physician 2013;42:867–70. - PubMed
-
- Karam G, Maillet F, Braud G, Battisti S, Hétet JF, Glémain P, Le Normand L, Bouchot O, Rigaud J. Surgical complications in kidney transplantation. Ann Urol (Paris) 2007;41:261–75. - PubMed
-
- Ruggiero R, Sparavigna L, Docimo G, Gubitosi A, Agresti M, Procaccini E, Docimo L. Post‐operative peritonitis due to anastomotic dehiscence after colonic resection. Multicentric experience, retrospective analysis of risk factors and review of the literature. Ann Ital Chir 2011;82:369–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

