IgE serum concentration against airborne fungi in children with respiratory allergies
- PMID: 27127524
- PMCID: PMC4848864
- DOI: 10.1186/s13223-016-0128-y
IgE serum concentration against airborne fungi in children with respiratory allergies
Abstract
Background: To evaluate total and specific E immunoglobulin (IgE) antibody concentrations in underage subjects with respiratory allergic diseases.
Methods: This study was a transversal-type study in 100 underage subjects between 4 and 14 years old, with asthma and/or allergic rhinitis. Total and specific IgE were quantified for airborne fungi in the city of São Luís, Maranhão, Brazil. Five distinct regions-North, South, Center, East and West-were selected so fungi could be collected monthly for 1 year. Twenty genera were identified. Aspergillus, Penicillium, Fusarium and Neurospora were selected for the preparation of sensitizing antigens from ELISA dishes. IgE total concentrations were estimated using the same method.
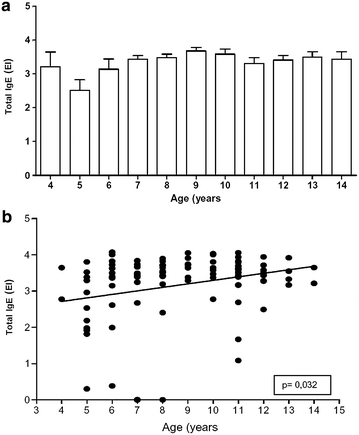
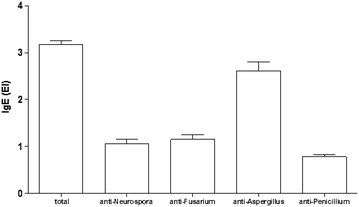
Results: IgE total serum concentration was increased in 97 % of the atopic subjects: 75 % of the subjects presented increased IgE anti-Aspergillus concentrations, 87 % presented IgE anti-Penicillium, 45 % presented IgE anti-Fusarium, and 46 % presented IgE anti-Neurospora.
Conclusions: Atopic subjects presented simultaneous IgE total and specific elevations for the tested fungi, possibly due to polysensitization caused by the presence of fungi in all of the areas all year. However, determining the clinical significance of the results was not yet possible because most of the data were isolated variables.
Keywords: Airborne fungi; IgE; Respiratory allergy.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

