Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula as a cause for symptomatic superficial siderosis: A report of two cases and review of the literature
- PMID: 27127712
- PMCID: PMC4828949
- DOI: 10.4103/2152-7806.179577
Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula as a cause for symptomatic superficial siderosis: A report of two cases and review of the literature
Abstract
Background: Superficial siderosis (SS) is the occult deposition of hemosiderin within the cerebral cortex due to repeat microhemorrhages within the central nervous system. The collection of hemosiderin within the pia and superficial cortical surface can lead to injury to the nervous tissue. The most common presentation is occult sensorineural hearing loss although many patients have been misdiagnosed with diseases such as multiple sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis before being diagnosed with SS. Only one case report exists in the literature describing an intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula (dAVF) as the putative cause for SS.
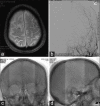
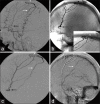
Case description: We describe two cases of SS caused by a dAVF. Both patients had a supratentorial, cortical lesion supplied by the middle meningeal artery with venous drainage into the superior sagittal sinus. In both patients, symptoms improved after endovascular embolization. The similar anatomic relationship of both dAVFs reported presents an interesting question about the pathogenesis of SS. Similar to the pathologic changes seen in the formation of intracranial arterial aneurysms; it would be possible that changes in the blood vessel lining and wall might predispose a patient to chronic, microhemorrhage resulting in SS.
Conclusions: We describe the second and third cases of a dAVF as the cause of SS, and the first cases of successful treatment of SS-associated dAVF with endovascular embolization. As noninvasive imaging techniques become more sensitive and easily obtained, one must consider their limitations in detecting occult intracranial vascular malformations such as dAVF as a possible etiology for SS.
Keywords: Dural arteriovenous fistula; embolization; superficial siderosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Evolution of angiographic signs of venous hypertension and clinical signs of intracranial hypertension in intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas].J Neuroradiol. 1999 Mar;26(1):49-58. J Neuroradiol. 1999. PMID: 10363442 French.
-
Spontaneous Resolution of Venous Aneurysms After Transarterial Embolization of a Variant Superior Sagittal Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: Case Report and Literature Review.Neurologist. 2017 Sep;22(5):186-195. doi: 10.1097/NRL.0000000000000137. Neurologist. 2017. PMID: 28859024 Review.
-
Clinical characteristics of dural arteriovenous fistula.J Clin Neurosci. 2002 Mar;9(2):147-55. doi: 10.1054/jocn.2001.1029. J Clin Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11922702
-
Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Presenting with Intracerebral Hemorrhage Associated with Chronological Angiographic Demonstration of Disturbed Leptomeningeal Venous Drainage as the Sole Outflow Route.World Neurosurg. 2016 Nov;95:617.e7-617.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2016.08.077. Epub 2016 Aug 24. World Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 27567578
-
First line direct access for transarterial embolization of a dural arteriovenous fistula: Case report and literature review.J Clin Neurosci. 2018 Feb;48:214-217. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2017.10.070. Epub 2017 Nov 11. J Clin Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29137915 Review.
Cited by
-
Low-Frequency Air-Bone Gap and Pulsatile Tinnitus Due to a Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: Considerations upon Possible Pathomechanisms and Literature Review.Audiol Res. 2023 Nov 1;13(6):833-844. doi: 10.3390/audiolres13060073. Audiol Res. 2023. PMID: 37987331 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Analysis of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Involving the Superior Sagittal Sinus: A Systematic Review.J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2021;15(1):1-7. doi: 10.5797/jnet.ra.2020-0085. Epub 2020 Sep 8. J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2021. PMID: 37503458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Idiopathic superficial siderosis of the central nervous system.Cerebellum Ataxias. 2021 Feb 25;8(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s40673-021-00133-5. Cerebellum Ataxias. 2021. PMID: 33632336 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson NE, Sheffield S, Hope JK. Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system: A late complication of cerebellar tumors. Neurology. 1999;52:163–9. - PubMed
-
- Cerqueira AC, Nardi AE, Bezerra JM. Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system: An unusual cause of sensorineural hearing loss. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2010;68:469–71. - PubMed
-
- Driver-Dunckley ED, Hoxworth JM, Patel NP, Bosch EP, Goodman BP. Superficial siderosis mimicking amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Clin Neuromuscul Dis. 2010;11:137–44. - PubMed
-
- Fearnley JM, Stevens JM, Rudge P. Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system. Brain. 1995;118(Pt 4):1051–66. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

