Dysregulation of ossification-related miRNAs in circulating osteogenic progenitor cells obtained from patients with aortic stenosis
- PMID: 27129184
- PMCID: PMC4876482
- DOI: 10.1042/CS20160094
Dysregulation of ossification-related miRNAs in circulating osteogenic progenitor cells obtained from patients with aortic stenosis
Abstract
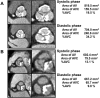
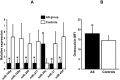
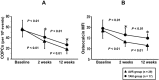
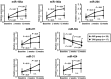
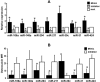
CAVD (calcific aortic valve disease) is the defining feature of AS (aortic stenosis). The present study aimed to determine whether expression of ossification-related miRNAs is related to differentiation intro COPCs (circulating osteogenic progenitor cells) in patients with CAVD. The present study included 46 patients with AS and 46 controls. Twenty-nine patients underwent surgical AVR (aortic valve replacement) and 17 underwent TAVI (transcatheter aortic valve implantation). The number of COPCs was higher in the AS group than in the controls (P<0.01). Levels of miR-30c were higher in the AS group than in the controls (P<0.01), whereas levels of miR-106a, miR-148a, miR-204, miR-211, miR-31 and miR-424 were lower in the AS group than in the controls (P<0.01). The number of COPCs and levels of osteocalcin protein in COPCs were positively correlated with levels of miR-30a and negatively correlated with levels of the remaining miRNAs (all P<0.05). The degree of aortic valve calcification was weakly positively correlated with the number of COPCs and miR-30c levels. The number of COPCs and miR-30c levels were decreased after surgery, whereas levels of the remaining miRNAs were increased (all P<0.05). Changes in these levels were greater after AVR than after TAVI (all P<0.05). In vitro study using cultured peripheral blood mononuclear cells transfected with each ossification-related miRNA showed that these miRNAs controlled levels of osteocalcin protein. In conclusion, dysregulation of ossification-related miRNAs may be related to the differentiation into COPCs and may play a significant role in the pathogenesis of CAVD.
Keywords: aortic valve replacement; calcific aortic valve disease; calcification; osteocalcin; transcatheter aortic valve implantation.
© 2016 The Author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Rajamannan N.M., Evans F.J., Aikawa E., Grande-Allen K.J., Demer L.L., Heistad D.D., Simmons C.A., Masters K.S., Mathieu P., O'Brien K.D., et al. Calcific aortic valve disease: not simply a degenerative process. Circulation. 2011;124:1783–1791. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.006767. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

