Rearrangement of the Extracellular Domain/Extracellular Loop 1 Interface Is Critical for Thyrotropin Receptor Activation
- PMID: 27129207
- PMCID: PMC4933169
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.709659
Rearrangement of the Extracellular Domain/Extracellular Loop 1 Interface Is Critical for Thyrotropin Receptor Activation
Abstract
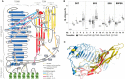
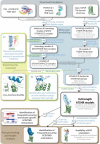
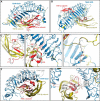
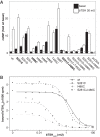
The thyroid stimulating hormone receptor (TSHR) is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) with a characteristic large extracellular domain (ECD). TSHR activation is initiated by binding of the hormone ligand TSH to the ECD. How the extracellular binding event triggers the conformational changes in the transmembrane domain (TMD) necessary for intracellular G protein activation is poorly understood. To gain insight in this process, the knowledge on the relative positioning of ECD and TMD and the conformation of the linker region at the interface of ECD and TMD are of particular importance. To generate a structural model for the TSHR we applied an integrated structural biology approach combining computational techniques with experimental data. Chemical cross-linking followed by mass spectrometry yielded 17 unique distance restraints within the ECD of the TSHR, its ligand TSH, and the hormone-receptor complex. These structural restraints generally confirm the expected binding mode of TSH to the ECD as well as the general fold of the domains and were used to guide homology modeling of the ECD. Functional characterization of TSHR mutants confirms the previously suggested close proximity of Ser-281 and Ile-486 within the TSHR. Rigidifying this contact permanently with a disulfide bridge disrupts ligand-induced receptor activation and indicates that rearrangement of the ECD/extracellular loop 1 (ECL1) interface is a critical step in receptor activation. The experimentally verified contact of Ser-281 (ECD) and Ile-486 (TMD) was subsequently utilized in docking homology models of the ECD and the TMD to create a full-length model of a glycoprotein hormone receptor.
Keywords: G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR); cell signaling; computer modeling; mass spectrometry (MS); protein cross-linking; receptor structure-function; site-directed mutagenesis; structural biology; surface plasmon resonance (SPR).
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Pierce J. G., and Parsons T. F. (1981) Glycoprotein hormones: structure and function. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 50, 465–495 - PubMed
-
- Jiang X., Dreano M., Buckler D. R., Cheng S., Ythier A., Wu H., Hendrickson W. A., and el Tayar N. (1995) Structural predictions for the ligand-binding region of glycoprotein hormone receptors and the nature of hormone-receptor interactions. Structure 3, 1341–1353 - PubMed
-
- Kleinau G., and Krause G. (2009) Thyrotropin and homologous glycoprotein hormone receptors: structural and functional aspects of extracellular signaling mechanisms. Endocr. Rev. 30, 133–151 - PubMed
-
- Heitman L. H., Kleinau G., Brussee J., Krause G., and Ijzerman A. P. (2012) Determination of different putative allosteric binding pockets at the lutropin receptor by using diverse drug-like low molecular weight ligands. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 351, 326–336 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

