Characterization of the Interactions between Calmodulin and Death Receptor 5 in Triple-negative and Estrogen Receptor-positive Breast Cancer Cells: AN INTEGRATED EXPERIMENTAL AND COMPUTATIONAL STUDY
- PMID: 27129269
- PMCID: PMC4933462
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.727727
Characterization of the Interactions between Calmodulin and Death Receptor 5 in Triple-negative and Estrogen Receptor-positive Breast Cancer Cells: AN INTEGRATED EXPERIMENTAL AND COMPUTATIONAL STUDY
Erratum in
-
Characterization of the interactions between calmodulin and death receptor 5 in triple-negative and estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells. AN INTEGRATED EXPERIMENTAL AND COMPUTATIONAL STUDY.J Biol Chem. 2016 Nov 4;291(45):23489. doi: 10.1074/jbc.A116.727727. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27815452 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
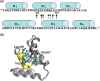
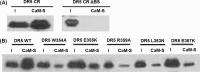
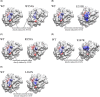
Activation of death receptor-5 (DR5) leads to the formation of death inducing signaling complex (DISC) for apoptotic signaling. Targeting DR5 to induce breast cancer apoptosis is a promising strategy to circumvent drug resistance and present a target for breast cancer treatment. Calmodulin (CaM) has been shown to regulate DR5-mediated apoptotic signaling, however, its mechanism remains unknown. In this study, we characterized CaM and DR5 interactions in breast cancer cells with integrated experimental and computational approaches. Results show that CaM directly binds to DR5 in a calcium dependent manner in breast cancer cells. The direct interaction of CaM with DR5 is localized at DR5 death domain. We have predicted and verified the CaM-binding site in DR5 being (354)WEPLMRKLGL(363) that is located at the α2 helix and the loop between α2 helix and α3 helix of DR5 DD. The residues of Trp-354, Arg-359, Glu-355, Leu-363, and Glu-367 in DR5 death domain that are important for DR5 recruitment of FADD and caspase-8 for DISC formation to signal apoptosis also play an important role for CaM-DR5 binding. The changed electrostatic potential distribution in the CaM-binding site in DR5 DD by the point mutations of W354A, E355K, R359A, L363N, or E367K in DR5 DD could directly contribute to the experimentally observed decreased CaM-DR5 binding by the point mutations of the key residues in DR5 DD. Results from this study provide a key step for the further investigation of the role of CaM-DR5 binding in DR5-mediated DISC formation for apoptosis in breast cancer cells.
Keywords: breast cancer; calmodulin (CaM); death domain; death receptor 5; electrostatics; integrated experimental and computational study; protein-protein interaction.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- DeSantis C., Siegel R., Bandi P., and Jemal A. (2011) Breast cancer statistics, 2011. CA Cancer J. Clin. 61, 409–418 - PubMed
-
- Guarneri V., and Conte P. F. (2004) The curability of breast cancer and the treatment of advanced disease. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 31, S149–161 - PubMed
-
- Siegel R., Desantis C., Virgo K., Stein K., Mariotto A., Smith T., Cooper D., Gansler T., Lerro C., Fedewa S., Lin C., Leach C., Cannady R. S., Cho H., Scoppa S., Hachey M., Kirch R., Jemal A., and Ward E. (2012) Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 62, 220–241. - PubMed
-
- Plasschaert S. L., Van Der Kolk D. M., De Bont E. S., Vellenga E., Kamps W. A., and De Vries E. G. (2004) Breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) in acute leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 45, 649–654 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

