MicroRNA-33 suppresses CCL2 expression in chondrocytes
- PMID: 27129293
- PMCID: PMC4859085
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20160068
MicroRNA-33 suppresses CCL2 expression in chondrocytes
Abstract
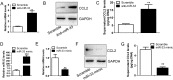
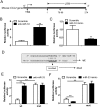
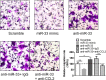
CCL2-mediated macrophage infiltration in articular tissues plays a pivotal role in the development of the osteoarthritis (OA). miRNAs regulate the onset and progression of diseases via controlling the expression of a series of genes. How the CCL2 gene was regulated by miRNAs was still not fully elucidated. In the present study, we demonstrated that the binding sites of miR-33 in the 3'UTR of CCL2 gene were conserved in human, mouse and rat species. By performing gain- or loss-of-function studies, we verified that miR-33 suppressed CCL2 expression in the mRNA and protein levels. We also found that miR-33 suppressed the CCL2 levels in the supernatant of cultured primary mouse chondrocytes. With reporter gene assay, we demonstrated that miR-33 targeted at AAUGCA in the 3'UTR of CCL2 gene. In transwell migration assays, we demonstrated that the conditional medium (CM) from miR-33 deficient chondrocytes potentiated the monocyte chemotaxis in a CCL2 dependent manner. Finally, we demonstrated that the level of miR-33 was decreased, whereas the CCL2 level was increased in the articular cartilage from the OA patients compared with the control group. In summary, we identified miR-33 as a novel suppressor of CCL2 in chondrocytes. The miR-33/CCL2 axis in chondrocytes regulates monocyte chemotaxis, providing a potential mechanism of macrophage infiltration in OA.
Keywords: CCL2; chemotaxis; microRNA-124 (miR-124); microRNA-33 (miR-33); osteoarthritis; reporter gene.
© 2016 The Author(s).
Figures


References
-
- Kunisch E., Kinne R.W., Alsalameh R.J., Alsalameh S. Pro-inflammatory IL-1beta and/or TNF-alpha up-regulate matrix metalloproteases-1 and -3 mRNA in chondrocyte subpopulations potentially pathogenic in osteoarthritis: in situ hybridization studies on a single cell level. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. doi:10.1111/1756-185X.12431. 2014 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

