Prevalence of pseudoresistant hypertension due to inaccurate blood pressure measurement
- PMID: 27129931
- PMCID: PMC4905807
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jash.2016.03.186
Prevalence of pseudoresistant hypertension due to inaccurate blood pressure measurement
Abstract
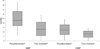
The prevalence of pseudoresistant hypertension (HTN) due to inaccurate BP measurement remains unknown. Triage BP measurements and measurements obtained at the same clinic visit by trained physicians were compared in consecutive adult patients referred for uncontrolled resistant HTN (RHTN). Triage BP measurements were taken by the clinic staff during normal intake procedures. BP measurements were obtained by trained physicians using the BpTRU (VSM Med Tech Ltd. Coquitlam, Canada) device. The prevalence of uncontrolled RHTN and differences in BP measurements were compared. Of 130 patients with uncontrolled RHTN, 33.1% (n = 43) were falsely identified as having uncontrolled RHTN based on triage BP measurements. The median (inter-quartile range) of differences in systolic BP between pseudoresistant and true resistant groups were 23 (17-33) mm Hg and 13 (6-21) mm Hg, respectively (P = .0001). The median (inter-quartile range) of differences in diastolic BP between the two groups were 12 (7-18) mm Hg and 8 (4-11) mm Hg, respectively (P = .001). Triage BP technique overestimated the prevalence of uncontrolled RHTN in approximately 33% of the patients emphasizing the importance of obtaining accurate BP measurements.
Keywords: Blood pressure; blood pressure measurement technique; pseudoresistant hypertension; resistant hypertension.
Copyright © 2016 American Society of Hypertension. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, Cushman WC, Dennison-Himmelfarb C, Handler J, Lackland DT, LeFevre ML, MacKenzie TD, Ogedegbe O, Smith SC, Jr, Svetkey LP, Taler SJ, Townsend RR, Wright JT, Jr, Narva AS, Ortiz E. 2014 evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8) JAMA. 2014;311(5):507–520. - PubMed
-
- Calhoun DA, Jones D, Textor S, Goff DC, Murphy TP, Toto RD, White A, Cushman WC, White W, Sica D, Ferdinand K, Giles TD, Falkner B, Carey RM American Heart Association Professional Education Committee. Resistant HTN: diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Professional Education Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research. Circulation. 2008;117(25):e510–e526. - PubMed
-
- de la Sierra A, Segura J, Banegas JR, Gorostidi M, de la Cruz JJ, Armario P, Oliveras A, Ruilope LM. Clinical features of 8295 patients with resistant HTN classified on the basis of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. Hypertension. 2011;57(5):898–902. - PubMed
-
- Pickering TG, Hall JE, Appel LJ, Falkner BE, Graves J, Hill MN, Jones DW, Kurtz T, Sheps SG, Roccella EJ. Recommendations for blood pressure measurement in humans and experimental animals: part 1: blood pressure measurement in humans: a statement for professionals from the Subcommittee of Professional and Public Education of the American Heart Association Council on High Blood Pressure Research. Circulation. 2005;111(5):697–716. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

