HUWE1 mutations in Juberg-Marsidi and Brooks syndromes: the results of an X-chromosome exome sequencing study
- PMID: 27130160
- PMCID: PMC4854010
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-009537
HUWE1 mutations in Juberg-Marsidi and Brooks syndromes: the results of an X-chromosome exome sequencing study
Abstract
Background: X linked intellectual disability (XLID) syndromes account for a substantial number of males with ID. Much progress has been made in identifying the genetic cause in many of the syndromes described 20-40 years ago. Next generation sequencing (NGS) has contributed to the rapid discovery of XLID genes and identifying novel mutations in known XLID genes for many of these syndromes.
Methods: 2 NGS approaches were employed to identify mutations in X linked genes in families with XLID disorders. 1 involved exome sequencing of genes on the X chromosome using the Agilent SureSelect Human X Chromosome Kit. The second approach was to conduct targeted NGS sequencing of 90 known XLID genes.
Results: We identified the same mutation, a c.12928 G>C transversion in the HUWE1 gene, which gives rise to a p.G4310R missense mutation in 2 XLID disorders: Juberg-Marsidi syndrome (JMS) and Brooks syndrome. Although the original families with these disorders were considered separate entities, they indeed overlap clinically. A third family was also found to have a novel HUWE1 mutation.
Conclusions: As we identified a HUWE1 mutation in an affected male from the original family reported by Juberg and Marsidi, it is evident the syndrome does not result from a mutation in ATRX as reported in the literature. Additionally, our data indicate that JMS and Brooks syndromes are allelic having the same HUWE1 mutation.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/
Figures

 , proband;
, proband;  , affected;
, affected;  , carrier.
, carrier.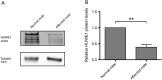



References
-
- Stevenson R, Schwartz C, Rogers C. Atlas of X-linked intellectual disability syndromes. New York: Oxford University Press, 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
