G-DOC Plus - an integrative bioinformatics platform for precision medicine
- PMID: 27130330
- PMCID: PMC4851789
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-016-1010-0
G-DOC Plus - an integrative bioinformatics platform for precision medicine
Abstract
Background: G-DOC Plus is a data integration and bioinformatics platform that uses cloud computing and other advanced computational tools to handle a variety of biomedical BIG DATA including gene expression arrays, NGS and medical images so that they can be analyzed in the full context of other omics and clinical information.
Results: G-DOC Plus currently holds data from over 10,000 patients selected from private and public resources including Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO), The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and the recently added datasets from REpository for Molecular BRAin Neoplasia DaTa (REMBRANDT), caArray studies of lung and colon cancer, ImmPort and the 1000 genomes data sets. The system allows researchers to explore clinical-omic data one sample at a time, as a cohort of samples; or at the level of population, providing the user with a comprehensive view of the data. G-DOC Plus tools have been leveraged in cancer and non-cancer studies for hypothesis generation and validation; biomarker discovery and multi-omics analysis, to explore somatic mutations and cancer MRI images; as well as for training and graduate education in bioinformatics, data and computational sciences. Several of these use cases are described in this paper to demonstrate its multifaceted usability.
Conclusion: G-DOC Plus can be used to support a variety of user groups in multiple domains to enable hypothesis generation for precision medicine research. The long-term vision of G-DOC Plus is to extend this translational bioinformatics platform to stay current with emerging omics technologies and analysis methods to continue supporting novel hypothesis generation, analysis and validation for integrative biomedical research. By integrating several aspects of the disease and exposing various data elements, such as outpatient lab workup, pathology, radiology, current treatments, molecular signatures and expected outcomes over a web interface, G-DOC Plus will continue to strengthen precision medicine research. G-DOC Plus is available at: https://gdoc.georgetown.edu .
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Cloud computing; Genotype-phenotype integration; Next generation sequencing; Outcomes research; Precision medicine; Translational research; Variant analysis.
Figures



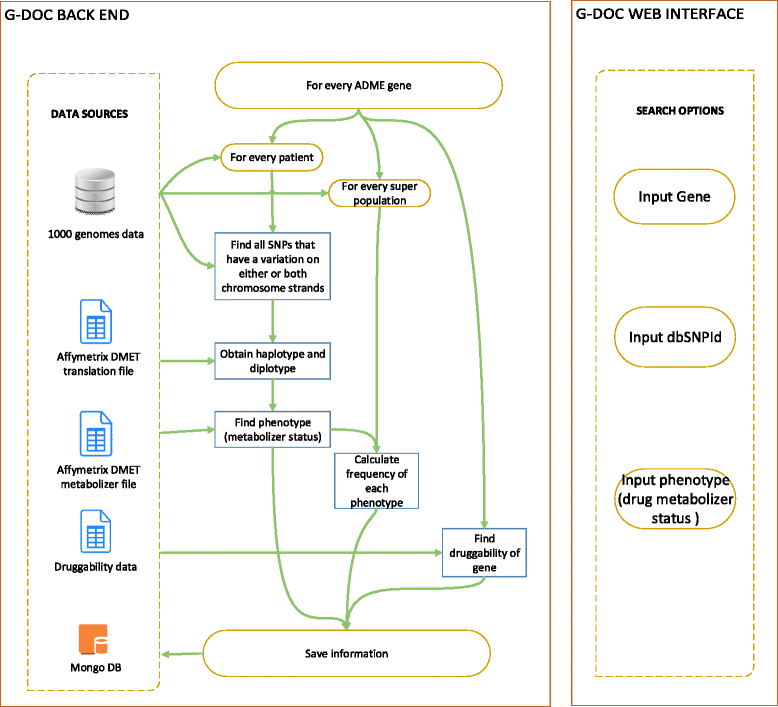
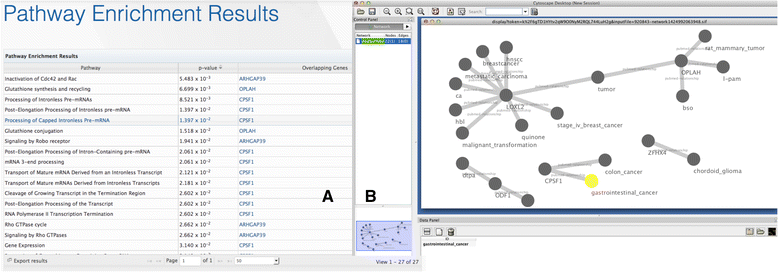
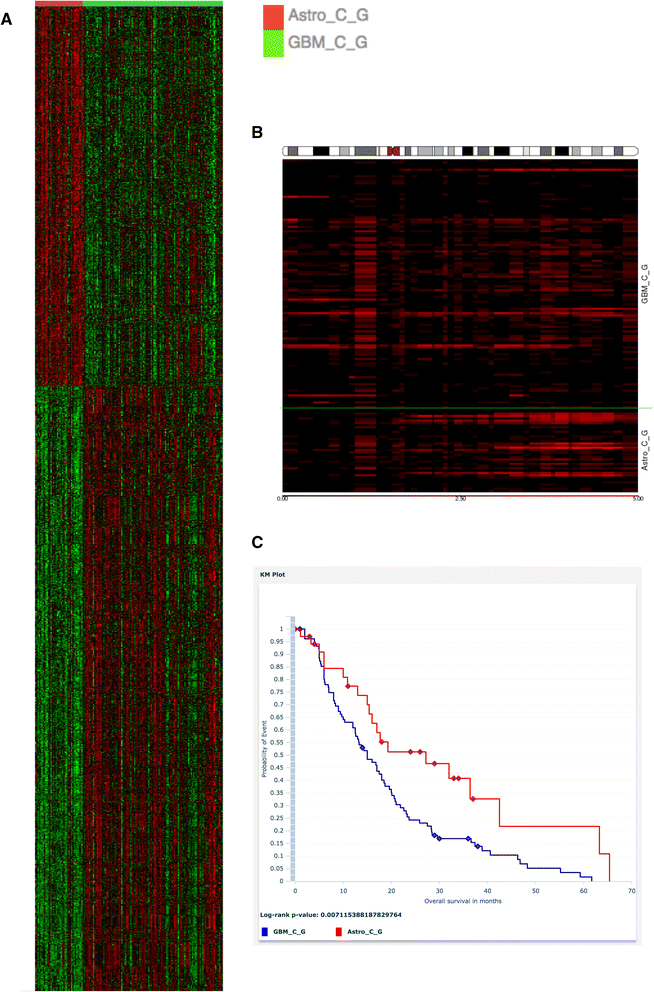

References
-
- Editorial. Method of the Year. Nature methods. 2008;5:1. - PubMed
-
- The 1000 genomes data. [http://www.1000genomes.org/] Accessed 7 Oct 2015.
-
- Complete Genomics. [http://www.completegenomics.com] Accessed 9 Feb 2015.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

