A Mechanistic Review of Cell Death in Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury
- PMID: 27130888
- PMCID: PMC5455778
- DOI: 10.1111/acer.13078
A Mechanistic Review of Cell Death in Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury
Abstract
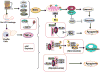
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) is a major health problem in the United States and worldwide without successful treatments. Chronic alcohol consumption can lead to ALD, which is characterized by steatosis, inflammation, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer. Recent studies suggest that alcohol induces both cell death and adaptive cell survival pathways in the liver, and the balance of cell death and cell survival ultimately decides the pathogenesis of ALD. This review summarizes the recent progress on the role and mechanisms of apoptosis, necroptosis, and autophagy in the pathogenesis of ALD. Understanding the complex regulation of apoptosis, necrosis, and autophagy may help to develop novel therapeutic strategies by targeting all 3 pathways simultaneously.
Keywords: Alcohol; Apoptosis; Autophagy; Liver Injury; Necroptosis.
Copyright © 2016 by the Research Society on Alcoholism.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors have no conflict of interest to claim.
Figures
References
-
- Bailey SM, Cunningham CC. Contribution of mitochondria to oxidative stress associated with alcoholic liver disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002;32:11–16. - PubMed
-
- Beckemeier ME, Bora PS. Fatty acid ethyl esters: potentially toxic products of myocardial ethanol metabolism. Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology. 1998;30:2487–2494. - PubMed
-
- Bourogaa E, Nciri R, Mezghani-Jarraya R, Racaud-Sultan C, Damak M, El Feki A. Antioxidant activity and hepatoprotective potential of Hammada scoparia against ethanol-induced liver injury in rats. J Physiol Biochem. 2013;69:227–237. - PubMed
-
- Casey CA, Kragskow SL, Sorrell MF, Tuma DJ. Chronic ethanol administration impairs the binding and endocytosis of asialo-orosomucoid in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:2704–2710. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

