A 3D Monte Carlo Method for Estimation of Patient-specific Internal Organs Absorbed Dose for (99m)Tc-hynic-Tyr(3)-octreotide Imaging
- PMID: 27134562
- PMCID: PMC4809152
- DOI: 10.4103/1450-1147.174700
A 3D Monte Carlo Method for Estimation of Patient-specific Internal Organs Absorbed Dose for (99m)Tc-hynic-Tyr(3)-octreotide Imaging
Abstract
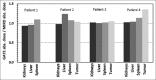
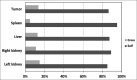
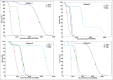
Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)-based tracers are easily available and more widely used than positron emission tomography (PET)-based tracers, and SPECT imaging still remains the most prevalent nuclear medicine imaging modality worldwide. The aim of this study is to implement an image-based Monte Carlo method for patient-specific three-dimensional (3D) absorbed dose calculation in patients after injection of (99m)Tc-hydrazinonicotinamide (hynic)-Tyr(3)-octreotide as a SPECT radiotracer. (99m)Tc patient-specific S values and the absorbed doses were calculated with GATE code for each source-target organ pair in four patients who were imaged for suspected neuroendocrine tumors. Each patient underwent multiple whole-body planar scans as well as SPECT imaging over a period of 1-24 h after intravenous injection of (99m)hynic-Tyr(3)-octreotide. The patient-specific S values calculated by GATE Monte Carlo code and the corresponding S values obtained by MIRDOSE program differed within 4.3% on an average for self-irradiation, and differed within 69.6% on an average for cross-irradiation. However, the agreement between total organ doses calculated by GATE code and MIRDOSE program for all patients was reasonably well (percentage difference was about 4.6% on an average). Normal and tumor absorbed doses calculated with GATE were slightly higher than those calculated with MIRDOSE program. The average ratio of GATE absorbed doses to MIRDOSE was 1.07 ± 0.11 (ranging from 0.94 to 1.36). According to the results, it is proposed that when cross-organ irradiation is dominant, a comprehensive approach such as GATE Monte Carlo dosimetry be used since it provides more reliable dosimetric results.
Keywords: GATE Monte Carlo package; MIRDOSE; S value; patient-specific dosimetry.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prediction of Absorbed Dose to Normal Organs with Endocrine Tumors for I-131 by use of 99mTC Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography/Computed Tomography and Geant4 Application for Tomographic Emission Simulation.Indian J Nucl Med. 2021 Jul-Sep;36(3):273-281. doi: 10.4103/ijnm.ijnm_6_21. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Indian J Nucl Med. 2021. PMID: 34658551 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-specific dosimetry of 99mTc-HYNIC-Tyr3-Octreotide in children.EJNMMI Phys. 2017 Oct 13;4(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s40658-017-0191-6. EJNMMI Phys. 2017. PMID: 29030760 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-specific radiation dosimetry of 99mTc-HYNIC-Tyr3-octreotide in neuroendocrine tumors.J Nucl Med. 2011 Sep;52(9):1474-81. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.111.088203. Epub 2011 Jul 27. J Nucl Med. 2011. PMID: 21795364
-
Simplified image-based dosimetry using planar images and patient-specific S-values.Med Phys. 2024 Aug;51(8):5708-5721. doi: 10.1002/mp.16974. Epub 2024 Feb 10. Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38340367
-
Comparison of internal dose estimates obtained using organ-level, voxel S value, and Monte Carlo techniques.Med Phys. 2014 Sep;41(9):092501. doi: 10.1118/1.4892606. Med Phys. 2014. PMID: 25186410
Cited by
-
Quantification of internal dosimetry in PET patients: individualized Monte Carlo vs generic phantom-based calculations.Med Phys. 2020 Sep;47(9):4574-4588. doi: 10.1002/mp.14344. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Med Phys. 2020. PMID: 32569389 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating the Absorbed Dose of Organs in Pediatric Imaging of 99mTc-DTPATc-DTPA Radiopharmaceutical using MIRDOSE Software.J Biomed Phys Eng. 2019 Jun 1;9(3):285-294. doi: 10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.984. eCollection 2019 Jun. J Biomed Phys Eng. 2019. PMID: 31341874 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Absorbed Dose to Normal Organs with Endocrine Tumors for I-131 by use of 99mTC Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography/Computed Tomography and Geant4 Application for Tomographic Emission Simulation.Indian J Nucl Med. 2021 Jul-Sep;36(3):273-281. doi: 10.4103/ijnm.ijnm_6_21. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Indian J Nucl Med. 2021. PMID: 34658551 Free PMC article.
-
Specific Absorbed Fractions of Internal Photon and Electron Emitters in a Human Voxel-based Phantom: A Monte Carlo Study.World J Nucl Med. 2017 Apr-Jun;16(2):114-121. doi: 10.4103/1450-1147.203065. World J Nucl Med. 2017. PMID: 28553177 Free PMC article.
-
Deformable torso phantoms of Chinese adults for personalized anatomy modelling.J Anat. 2018 Jul;233(1):121-134. doi: 10.1111/joa.12815. Epub 2018 Apr 16. J Anat. 2018. PMID: 29663370 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grimes J, Celler A, Birkenfeld B, Shcherbinin S, Listewnik MH, Piwowarska-Bilska H, et al. Patient-specific radiation dosimetry of 99m Tc-HYNIC-Tyr 3 -octreotide in neuroendocrine tumors. J Nucl Med. 2011;52:1474–81. - PubMed
-
- Decristoforo C, Mather SJ, Cholewinski W, Donnemiller E, Riccabona G, Moncayo R. 99m Tc-EDDA/HYNIC-TOC: A new 99m Tc-labelled radiopharmaceutical for imaging somatostatin receptor-positive tumours; first clinical results and intra-patient comparison with 111 In-labelled octreotide derivatives. Eur J Nucl Med. 2000;27:1318–25. - PubMed
-
- Plachcinska A, Mikolajczak R, Maecke HR, Mlodkowska E, Kunert-Radek J, Michalski A, et al. Clinical usefulness of 99m Tc-EDDA/HYNIC-TOC scintigraphy in oncological diagnostics: A preliminary communication. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2003;30:1402–6. - PubMed
-
- Putzer D, Kroiss A, Waitz D, Gabriel M, Traub-Weidinger T, Uprimny C, et al. Somatostatin receptor PET in neuroendocrine tumours: 68 Ga-DOTA0, Tyr 3 -octreotide versus 68 Ga-DOTA0-lanreotide. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013;40:364–72. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

