Highly scalable, closed-loop synthesis of drug-loaded, layer-by-layer nanoparticles
- PMID: 27134622
- PMCID: PMC4847955
- DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201504385
Highly scalable, closed-loop synthesis of drug-loaded, layer-by-layer nanoparticles
Abstract
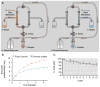
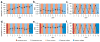
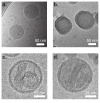
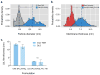
Layer-by-layer (LbL) self-assembly is a versatile technique from which multicomponent and stimuli-responsive nanoscale drug carriers can be constructed. Despite the benefits of LbL assembly, the conventional synthetic approach for fabricating LbL nanoparticles requires numerous purification steps that limit scale, yield, efficiency, and potential for clinical translation. In this report, we describe a generalizable method for increasing throughput with LbL assembly by using highly scalable, closed-loop diafiltration to manage intermediate purification steps. This method facilitates highly controlled fabrication of diverse nanoscale LbL formulations smaller than 150 nm composed from solid-polymer, mesoporous silica, and liposomal vesicles. The technique allows for the deposition of a broad range of polyelectrolytes that included native polysaccharides, linear polypeptides, and synthetic polymers. We also explore the cytotoxicity, shelf life and long-term storage of LbL nanoparticles produced using this approach. We find that LbL coated systems can be reliably and rapidly produced: specifically, LbL-modified liposomes could be lyophilized, stored at room temperature, and reconstituted without compromising drug encapsulation or particle stability, thereby facilitating large scale applications. Overall, this report describes an accessible approach that significantly improves the throughput of nanoscale LbL drug-carriers that show low toxicity and are amenable to clinically relevant storage conditions.
Keywords: biomaterials; colloid chemistry; layer-by-layer nanoparticles; polymer engineering; scalable synthesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Engineering nanolayered particles for modular drug delivery.J Control Release. 2016 Oct 28;240:364-386. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.01.040. Epub 2016 Jan 22. J Control Release. 2016. PMID: 26809005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Composite Layer-by-Layer (LBL) assembly with inorganic nanoparticles and nanowires.Acc Chem Res. 2008 Dec;41(12):1831-41. doi: 10.1021/ar8001377. Acc Chem Res. 2008. PMID: 19053241
-
Stimuli-sensitive layer-by-layer (LbL) self-assembly systems: targeting and biosensory applications.J Control Release. 2013 Mar 28;166(3):294-306. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.12.033. Epub 2013 Jan 8. J Control Release. 2013. PMID: 23313111 Review.
-
Effects of polymer end-group chemistry and order of deposition on controlled protein delivery from layer-by-layer assembly.Biomacromolecules. 2013 Mar 11;14(3):794-800. doi: 10.1021/bm3018559. Epub 2013 Feb 11. Biomacromolecules. 2013. PMID: 23360295
-
Sonication-assisted Layer-by-Layer self-assembly nanoparticles for resveratrol delivery.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019 Dec;105:110022. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.110022. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019. PMID: 31546400
Cited by
-
Development of a Pemetrexed/Folic Acid Nanoformulation: Synthesis, Characterization, and Efficacy in a Murine Colorectal Cancer Model.ACS Omega. 2020 Jun 16;5(25):15424-15432. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c01550. eCollection 2020 Jun 30. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 32637817 Free PMC article.
-
Layer-by-layer nanoparticles for novel delivery of cisplatin and PARP inhibitors for platinum-based drug resistance therapy in ovarian cancer.Bioeng Transl Med. 2019 Jun 14;4(2):e10131. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10131. eCollection 2019 May. Bioeng Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31249881 Free PMC article.
-
Surfactant-Mediated Assembly of Precision-Size Liposomes.Chem Mater. 2024 Jul 25;36(15):7263-7273. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.4c01127. eCollection 2024 Aug 13. Chem Mater. 2024. PMID: 39156714 Free PMC article.
-
Trafficking through the blood-brain barrier is directed by core and outer surface components of layer-by-layer nanoparticles.Bioeng Transl Med. 2023 Dec 28;9(4):e10636. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10636. eCollection 2024 Jul. Bioeng Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 39036092 Free PMC article.
-
Massively parallel pooled screening reveals genomic determinants of nanoparticle delivery.Science. 2022 Jul 22;377(6604):eabm5551. doi: 10.1126/science.abm5551. Epub 2022 Jul 22. Science. 2022. PMID: 35862544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schroeder A, Heller DA, Winslow MM, Dahlman JE, Pratt GW, Langer R, Jacks T, Anderson DG. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12:39–50. - PubMed
-
- Caruso F. Adv Mater. 2001:13.
- Hammond PT. Adv Mater. 2004;16:1271–1293.
- Hammond PT. Nanomedicine. 2012;7:619–622. - PubMed
-
- Poon Z, Lee JB, Morton SW, Hammond PT. Nano Lett. 2011;11:2096–2103. - PMC - PubMed
- Morton SW, Shah NJ, Quadir MA, Deng ZJ, Poon Z, Hammond PT. Adv Healthcare Mater. 2014;3:867–875. - PMC - PubMed
- Wang Y, Yan Y, Cui J, Hosta-Rigau L, Heath JK, Nice EC, Caruso F. Adv Mater. 2010;22:4293–4297. - PubMed
- Fujimoto K, Toyoda T, Fukui Y. Macromolecules. 2007;40:5122–5128.
- Gittins DI, Caruso F. J Phys Chem B. 2001;105:6846–6852.
- Morton SW, Poon Z, Hammond PT. Biomaterials. 2013;34:5328–5335. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Elbakry A, Zaky A, Liebl R, Rachel R, Goepferich A, Breunig M. Nano Lett. 2009;9:2059–2064. - PubMed
- Poon Z, Chang D, Zhao X, Hammond PT. ACS Nano. 2011;5:4284–4292. - PMC - PubMed
- Shutava TG, Balkundi SS, Vangala P, Steffan JJ, Bigelow RL, Cardelli JA, O'Neal DP, Lvov YM. ACS Nano. 2009;3:1877–1885. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
