Low Dimensionality in Gene Expression Data Enables the Accurate Extraction of Transcriptional Programs from Shallow Sequencing
- PMID: 27135536
- PMCID: PMC4856162
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cels.2016.04.001
Low Dimensionality in Gene Expression Data Enables the Accurate Extraction of Transcriptional Programs from Shallow Sequencing
Abstract
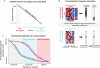
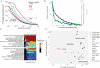
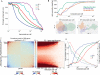
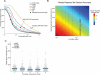
A tradeoff between precision and throughput constrains all biological measurements, including sequencing-based technologies. Here, we develop a mathematical framework that defines this tradeoff between mRNA-sequencing depth and error in the extraction of biological information. We find that transcriptional programs can be reproducibly identified at 1% of conventional read depths. We demonstrate that this resilience to noise of "shallow" sequencing derives from a natural property, low dimensionality, which is a fundamental feature of gene expression data. Accordingly, our conclusions hold for ∼350 single-cell and bulk gene expression datasets across yeast, mouse, and human. In total, our approach provides quantitative guidelines for the choice of sequencing depth necessary to achieve a desired level of analytical resolution. We codify these guidelines in an open-source read depth calculator. This work demonstrates that the structure inherent in biological networks can be productively exploited to increase measurement throughput, an idea that is now common in many branches of science, such as image processing.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Differential expression analysis of RNA sequencing data by incorporating non-exonic mapped reads.BMC Genomics. 2015;16 Suppl 7(Suppl 7):S14. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-16-S7-S14. Epub 2015 Jun 11. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26099631 Free PMC article.
-
Joint estimation of isoform expression and isoform-specific read distribution using multisample RNA-Seq data.Bioinformatics. 2014 Feb 15;30(4):506-13. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt704. Epub 2013 Dec 3. Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 24307704
-
Deep sequencing reveals cell-type-specific patterns of single-cell transcriptome variation.Genome Biol. 2015 Jun 9;16(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s13059-015-0683-4. Genome Biol. 2015. PMID: 26056000 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the next-generation sequencing data depth on various biological result inferences.Sci China Life Sci. 2013 Feb;56(2):104-9. doi: 10.1007/s11427-013-4441-0. Epub 2013 Feb 8. Sci China Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23393025 Review.
-
Seq-ing answers: uncovering the unexpected in global gene regulation.Curr Genet. 2018 Dec;64(6):1183-1188. doi: 10.1007/s00294-018-0839-3. Epub 2018 Apr 19. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 29675618 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Towards a definition of microglia heterogeneity.Commun Biol. 2022 Oct 20;5(1):1114. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-04081-6. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36266565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating Cellular Trajectories in the Severity of COVID-19 and Their Transcriptional Programs Using Machine Learning Approaches.Genes (Basel). 2021 Apr 24;12(5):635. doi: 10.3390/genes12050635. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33923155 Free PMC article.
-
Conditional generative adversarial network for gene expression inference.Bioinformatics. 2018 Sep 1;34(17):i603-i611. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty563. Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 30423066 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and Opportunities for the Translation of Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Technologies to Dermatology.Life (Basel). 2022 Jan 4;12(1):67. doi: 10.3390/life12010067. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35054460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thermoregulation via Temperature-Dependent PGD2 Production in Mouse Preoptic Area.Neuron. 2019 Jul 17;103(2):309-322.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.04.035. Epub 2019 May 28. Neuron. 2019. PMID: 31151773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bengio Y, Delalleau O, Roux NL, Paiement J-F, Vincent P, Ouimet M. Learning Eigenfunctions Links Spectral Embedding and Kernel PCA. Neural Computation. 2004;16:2197–2219. - PubMed
-
- Bergmann S, Ihmels J, Barkai N. Iterative signature algorithm for the analysis of large-scale gene expression data. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2003;67:031902. - PubMed
-
- Bonneau R. Learning biological networks: from modules to dynamics. Nat Chem Biol. 2008;4:658–664. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

