Primary intracranial neuroendocrine tumor: two case reports
- PMID: 27138163
- PMCID: PMC4852410
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-016-0887-4
Primary intracranial neuroendocrine tumor: two case reports
Abstract
Background: Neuroendocrine tumor originates from the diffuse neuroendocrine system. Intracranial originating is lower to 0.74 %.
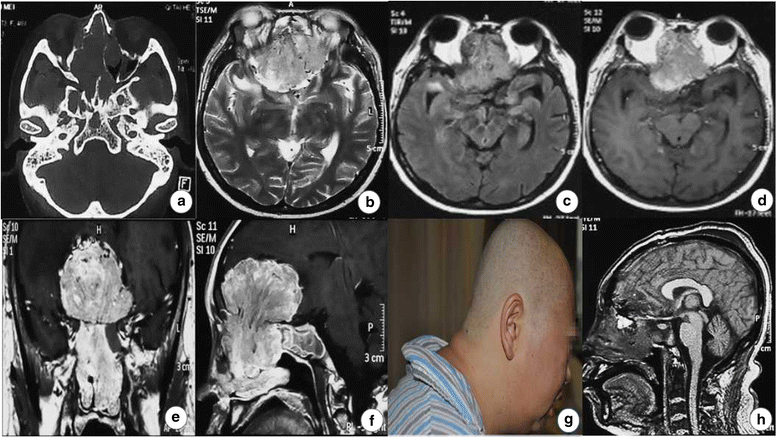
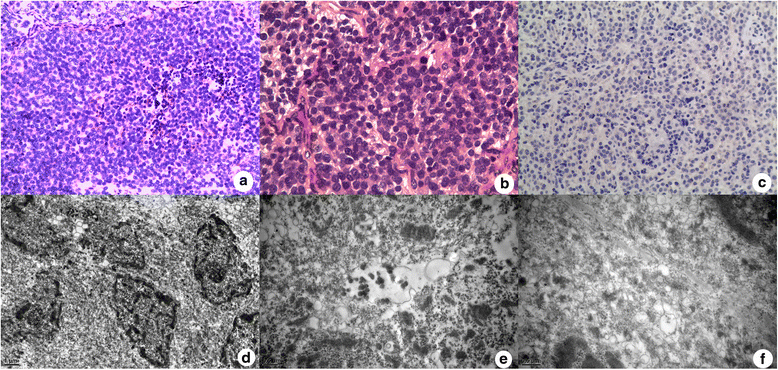
Case presentation: We present two cases of primary intracranial neuroendocrine tumor A 39-year-old woman was admitted with headache, fever, polydipsia and polyuria. Biochemical and endocrinological results showed hyponatremia, hypothyroidism and hypopituitarism. MRI scans demonstrated an obviouslyenhancing lesion in seller and superseller area. Then a gross removal of tumor was achieved during the single nostril transsphenoidal approach surgery. Pathological diagnosis was high-grade small-cell neuroendocrine tumor. A 40-year-old woman presented with multiple symptoms and neurological deficit. Neuroimaging results demonstrated a huge obviously-enhancing tumor in anterior cranial fossa. Biochemical and hormone findings revealed hypokalemia, high glucose and hypercortisolemia. The intracranial surgery achieved a gross removal through a right frontal craniotomy. Pathological diagnosis was low-grade small-cell neuroendocrine tumor with immuno-negativity for ACTH.
Conclusion: The mechanism, diagnosis, and treatment of neuroendocrine tumor are still challenging.
Keywords: Anterior skull base reconstruction; Diagnosis; Ectopic ACTH syndrome; Neuroendocrine tumor; Treatment.
Figures


References
-
- Jing S, Xu Z, Wang Z, et al. Pathological category and diagnosis of neuroendocrine tumor in nonneuroendocrine system. J Clin Exp Pathol. 2009;25:548–50.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

