Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles acutely promote thrombosis and cardiac oxidative stress and DNA damage in mice
- PMID: 27138375
- PMCID: PMC4852430
- DOI: 10.1186/s12989-016-0132-x
Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles acutely promote thrombosis and cardiac oxidative stress and DNA damage in mice
Abstract
Background: Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (USPIO) are being developed for several biomedical applications including drug delivery and imaging. However, little is known about their possible adverse effects on thrombosis and cardiac oxidative and DNA damage.
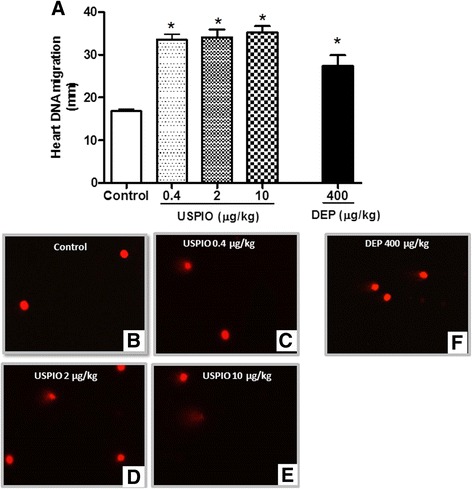
Methods: Presently, we investigated the acute (1 h) effect of intravenously (i.v.) administered USPIO in mice (0.4, 2 and 10 μg/kg). Diesel exhaust particles (DEP; 400 μg/kg) were used as positive control.
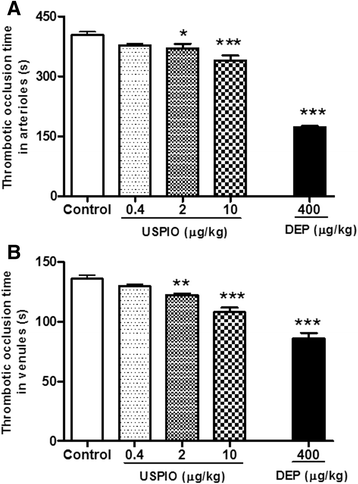
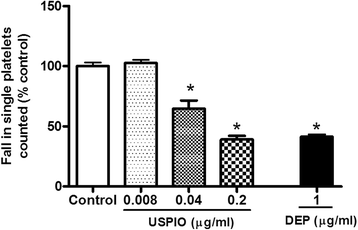
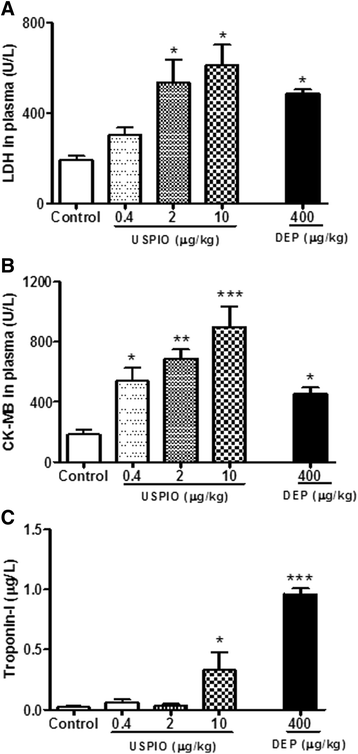
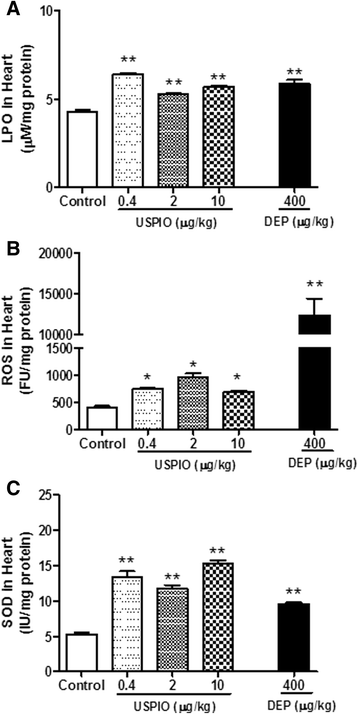
Results: USPIO induced a prothrombotic effect in pial arterioles and venules in vivo and increased the plasma plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1). Both thrombogenicity and PAI-1 concentration were increased by DEP. The direct addition of USPIO (0.008, 0.04 and 0.2 μg/ml) to untreated mouse blood dose-dependently induced in vitro platelet aggregation. USPIO caused a shortening of activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) and prothrombin time (PT). Similarly, DEP administration (1 μg/ml) triggered platelet aggregation in vitro in whole blood. DEP also reduced PT and aPTT. The plasma levels of creatine phosphokinase-MB isoenzyme (CK-MB), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and troponin-I were increased by USPIO. DEP induced a significant increase of CK-MB, LDH and troponin I levels in plasma. The cardiac levels of markers of oxidative stress including lipid peroxidation, reactive oxygen species and superoxide dismutase activity were increased by USPIO. Moreover, USPIO caused DNA damage in the heart. Likewise, DEP increased the markers of oxidative stress and induced DNA damage in the heart.
Conclusion: We conclude that acute i.v. administration of USPIO caused thrombosis and cardiac oxidative stress and DNA damage. These findings provide novel insight into the pathophysiological effects of USPIO on cardiovascular homeostasis, and highlight the need for a thorough evaluation of their toxicity.
Keywords: Comet assay; Oxidative stress; Thrombosis; Toxicity; Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Thrombosis and systemic and cardiac oxidative stress and DNA damage induced by pulmonary exposure to diesel exhaust particles and the effect of nootkatone thereon.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018 May 1;314(5):H917-H927. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00313.2017. Epub 2018 Jan 5. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29351455
-
The acute pulmonary and thrombotic effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles after intratracheal instillation in mice.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Apr 10;12:2913-2922. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S127180. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28435267 Free PMC article.
-
Exacerbation of thrombotic events by diesel exhaust particle in mouse model of hypertension.Toxicology. 2011 Jul 11;285(1-2):39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2011.03.018. Epub 2011 Apr 8. Toxicology. 2011. PMID: 21501650
-
Diesel Exhaust Particles Induce Impairment of Vascular and Cardiac Homeostasis in Mice: Ameliorative Effect of Emodin.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(4):1517-26. doi: 10.1159/000430315. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26159184
-
Diagnostic Applications of Ultrasmall Superparamagnetic Particles of Iron Oxide for Imaging Myocardial and Vascular Inflammation.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2021 Jun;14(6):1249-1264. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2020.06.038. Epub 2020 Aug 26. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2021. PMID: 32861658 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of DNA Damage and Oxidative Stress in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells Exposed to PM2.5 from Beijing, China, in Winter.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jul 6;17(13):4874. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17134874. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32640694 Free PMC article.
-
Nanotoxicity: a challenge for future medicine.Turk J Med Sci. 2020 Jun 23;50(4):1180-1196. doi: 10.3906/sag-1912-209. Turk J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32283898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of prolonged exposure to occasional and regular waterpipe smoke on cardiac injury, oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in male mice.Front Physiol. 2024 Feb 2;15:1286366. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1286366. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38370014 Free PMC article.
-
The Surface Amine Group of Ultrasmall Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Produce Analgesia in the Spinal Cord and Decrease Long-Term Potentiation.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Feb 6;14(2):366. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14020366. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35214098 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasmall iron oxide nanoparticles cause significant toxicity by specifically inducing acute oxidative stress to multiple organs.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2022 Mar 29;19(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12989-022-00465-y. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35351185 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Usman A, Sadat U, Patterson AJ, Tang TY, Varty K, Boyle JR, et al. Use of ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide particles for imaging carotid atherosclerosis. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015. [Epub ahead of print]. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

