Phase III Trial Evaluating Letrozole As First-Line Endocrine Therapy With or Without Bevacizumab for the Treatment of Postmenopausal Women With Hormone Receptor-Positive Advanced-Stage Breast Cancer: CALGB 40503 (Alliance)
- PMID: 27138575
- PMCID: PMC5012690
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2015.66.1595
Phase III Trial Evaluating Letrozole As First-Line Endocrine Therapy With or Without Bevacizumab for the Treatment of Postmenopausal Women With Hormone Receptor-Positive Advanced-Stage Breast Cancer: CALGB 40503 (Alliance)
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate whether anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy with bevacizumab prolongs progression-free survival (PFS) when added to first-line letrozole as treatment of hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer (MBC).
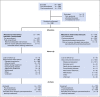
Patients and methods: Women with hormone receptor-positive MBC were randomly assigned 1:1 in a multicenter, open-label, phase III trial of letrozole (2.5 mg orally per day) with or without bevacizumab (15 mg/kg intravenously once every 3 weeks) within strata defined by measurable disease and disease-free interval. This trial had 90% power to detect a 50% improvement in median PFS from 6 to 9 months. Using a one-sided α = .025, a target sample size of 352 patients was planned.
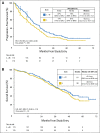
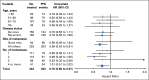
Results: From May 2008 to November 2011, 350 women were recruited; 343 received treatment and were observed for efficacy and safety. Median age was 58 years (range, 25 to 87 years). Sixty-two percent had measurable disease, and 45% had de novo MBC. At a median follow-up of 39 months, the addition of bevacizumab resulted in a significant reduction in the hazard of progression (hazard ratio, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.59 to 0.96; P = .016) and a prolongation in median PFS from 15.6 months with letrozole to 20.2 months with letrozole plus bevacizumab. There was no significant difference in overall survival (hazard ratio, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.65 to 1.18; P = .188), with median overall survival of 43.9 months with letrozole versus 47.2 months with letrozole plus bevacizumab. The largest increases in incidence of grade 3 to 4 treatment-related toxicities with the addition of bevacizumab were hypertension (24% v 2%) and proteinuria (11% v 0%).
Conclusion: The addition of bevacizumab to letrozole improved PFS in hormone receptor-positive MBC, but this benefit was associated with a markedly increased risk of grade 3 to 4 toxicities. Research on predictive markers will be required to clarify the role of bevacizumab in this setting.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00601900.
© 2016 by American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ disclosures of potential conflicts of interest are found in the article online at www.jco.org. contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406:747–752. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U10 CA031946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA033601/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180858/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180795/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180791/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180882/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180838/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180888/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA138561/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

