Association between Circulating Vitamin D Metabolites and Fecal Bile Acid Concentrations
- PMID: 27138789
- PMCID: PMC4993194
- DOI: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-16-0033
Association between Circulating Vitamin D Metabolites and Fecal Bile Acid Concentrations
Abstract
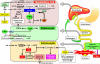
Although hydrophobic bile acids have been demonstrated to exhibit cytotoxic and carcinogenic effects in the colorectum, ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) has been investigated as a potential chemopreventive agent. Vitamin D has been shown to play a role in both bile acid metabolism and in the development of colorectal neoplasia. Using a cross-sectional design, we sought to determine whether baseline circulating concentrations of the vitamin D metabolites 25(OH)D and 1,25(OH)2D were associated with baseline fecal bile acid concentrations in a trial of UDCA for the prevention of colorectal adenoma recurrence. We also prospectively evaluated whether vitamin D metabolite concentrations modified the effect of UDCA on adenoma recurrence. After adjustment for age, sex, BMI, physical activity, and calcium intake, adequate concentrations of 25(OH)D (≥30 ng/mL) were statistically significantly associated with reduced odds for high levels of total [OR, 0.61; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.38-0.97], and primary (OR, 0.61; 95% CI, 0.38-0.96) bile acids, as well as individually with chenodeoxycholic acid (OR, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.24-0.63) and cholic acid (OR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.36-0.90). No significant associations were observed for 1,25(OH)2D and high versus low fecal bile acid concentrations. In addition, neither 25(OH)D nor 1,25(OH)2D modified the effect of UDCA on colorectal adenoma recurrence. In conclusion, this is the first study to demonstrate an inverse relationship between circulating levels of 25(OH)D and primary fecal bile acid concentrations. These results support prior data demonstrating that vitamin D plays a key role in bile acid metabolism, and suggest a potential mechanism of action for 25(OH)D in colorectal cancer prevention. Cancer Prev Res; 9(7); 589-97. ©2016 AACR.
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA: Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Steele CB, Rim SH, Joseph DA, King JB, Seeff LC. Colorectal cancer incidence and screening - United States, 2008 and 2010. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2013 Nov 22;62(Suppl 3):53–60. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein H, Bernstein C, Payne CM, Dvorakova K, Garewal H. Bile acids as carcinogens in human gastrointestinal cancers. Mut Res. 2005;589:47–65. - PubMed
-
- Barrasa JI, Olmo N, Lizarbe MA, Turnay J. Bile acids in the colon, from healthy to cytotoxic molecules. Toxicol In Vitro. Mar. 2013;27(2):964–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

