Imaging Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Modifications in Living Systems
- PMID: 27139586
- PMCID: PMC4900226
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2015.6415
Imaging Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Modifications in Living Systems
Abstract
Significance: Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) may regulate signaling, ion channels, transcription factors, and biosynthetic processes. ROS-related diseases can be due to either a shortage or an excess of ROS.
Recent advances: Since the biological activity of ROS depends on not only concentration but also spatiotemporal distribution, real-time imaging of ROS, possibly in vivo, has become a need for scientists, with potential for clinical translation. New imaging techniques as well as new contrast agents in clinically established modalities were developed in the previous decade.
Critical issues: An ideal imaging technique should determine ROS changes with high spatio-temporal resolution, detect physiologically relevant variations in ROS concentration, and provide specificity toward different redox couples. Furthermore, for in vivo applications, bioavailability of sensors, tissue penetration, and a high signal-to-noise ratio are additional requirements to be satisfied.
Future directions: None of the presented techniques fulfill all requirements for clinical translation. The obvious way forward is to incorporate anatomical and functional imaging into a common hybrid-imaging platform. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 24, 939-958.
Figures
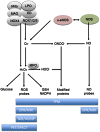

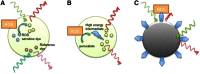
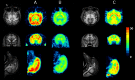

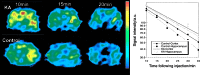
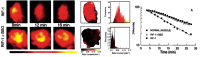
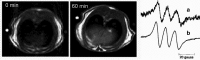
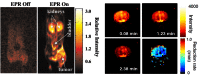
References
-
- Abbas K, Hardy M, Poulhès F, Karoui H, Tordo P, Ouari O, and Peyrot F. Detection of superoxide production in stimulated and unstimulated living cells using new cyclic nitrone spin traps. Free Radic Biol Med 71: 281–290, 2014 - PubMed
-
- Bacic G, Nilges MJ, Magin RL, Walczak T, and Swartz HM. In vivo localized ESR spectroscopy reflecting metabolism. Magn Reson Med 10: 266–272, 1989 - PubMed
-
- Ballinger JR. Imaging hypoxia in tumors. Semin Nucl Med 31: 321–329, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
