Effect of Irradiation on Microparticles in Red Blood Cell Concentrates
- PMID: 27139610
- PMCID: PMC4855057
- DOI: 10.3343/alm.2016.36.4.362
Effect of Irradiation on Microparticles in Red Blood Cell Concentrates
Abstract
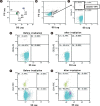
Changes in microparticles (MP) from red blood cell (RBC) concentrates in the context of irradiation have not been investigated. The aim of this study was to evaluate how irradiation affects the number of MPs within transfusion components. Twenty RBC concentrates, within 14 days after donation, were exposed to gamma rays (dose rate: 25 cGy) from a cesium-137 irradiator. Flow cytometry was used to determine the numbers of MPs derived from RBC concentrates before and 24 hr after irradiation. The mean number of MPs (±standard deviation) in RBC concentrates was 21.9×10⁹/L (±22.7×10⁹/L), and the total number of MPs ranged from 2.6×10⁹/L to 96.9×10⁹/L. The mean number of MPs increased to 22.6×10⁹/L (±31.6×10⁹/L) after irradiation. Before irradiation, the CD41-positive and CD235a-positive MPs constituted 9.5% (1.0×10⁹/L) and 2.2% (263×10⁶/L) of total MPs, respectively. After irradiation, CD41-positive MPs increased to 12.1% (1.5×10⁹/L) (P=0.014), but the CD235a-positive MPs decreased to 2.0% (214×10⁶/L) of the total MPs (P=0.369). Irradiation increases the number of CD41-positive MPs within RBC concentrates, suggesting the irradiation of RBC concentrates could be associated with thrombotic risk of circulating blood through the numerical change.
Keywords: CD235a; CD41; Irradiation; Microparticles; RBCs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microparticles in stored canine RBC concentrates.Vet Clin Pathol. 2013 Jun;42(2):163-9. doi: 10.1111/vcp.12034. Epub 2013 Apr 5. Vet Clin Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23560818
-
Evaluation of microparticles in whole blood by multicolour flow cytometry assay.Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2013 Apr;73(3):229-39. doi: 10.3109/00365513.2013.769278. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2013. PMID: 23452203
-
Flow rate calibration to determine cell-derived microparticles and homogeneity of blood components.Transfus Apher Sci. 2017 Aug;56(4):585-590. doi: 10.1016/j.transci.2017.07.016. Epub 2017 Jul 18. Transfus Apher Sci. 2017. PMID: 28774828
-
Influence of red blood cell-derived microparticles upon vasoregulation.Blood Transfus. 2017 Oct;15(6):522-534. doi: 10.2450/2017.0353-16. Epub 2017 May 15. Blood Transfus. 2017. PMID: 28686154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelet microparticles and vascular cells interactions: a checkpoint between the haemostatic and thrombotic responses.Platelets. 2008 Feb;19(1):9-23. doi: 10.1080/09537100701817232. Platelets. 2008. PMID: 18231934 Review.
Cited by
-
Red Blood Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: An Overview of Current Research Progress, Challenges, and Opportunities.Biomedicines. 2023 Oct 16;11(10):2798. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102798. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37893171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of exosomes released from apheresis platelet concentrates under the impact of gamma irradiation and storage time upon platelet aggregation and hemostasis.Blood Transfus. 2023 May;21(3):257-267. doi: 10.2450/2022.006-22. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Blood Transfus. 2023. PMID: 35969141 Free PMC article.
-
Red cell extracellular vesicles and coagulation activation pathways.Curr Opin Hematol. 2023 Nov 1;30(6):194-202. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000780. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Curr Opin Hematol. 2023. PMID: 37548370 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ayers L, Kohler M, Harrison P, Sargent I, Dragovic R, Schaap M, et al. Measurement of circulating cell-derived microparticles by flow cytometry: sources of variability within the assay. Thromb Res. 2011;127:370–377. - PubMed
-
- Jung KH, Chu K, Lee ST, Park HK, Bahn JJ, Kim DH, et al. Circulating endothelial microparticles as a marker of cerebrovascular disease. Ann Neurol. 2009;66:191–199. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

