Intraoral Pseudo-Onion Bulb Intraneural Proliferations in a Patient with Hemimandibular Hyperplasia: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- PMID: 27140175
- PMCID: PMC5082049
- DOI: 10.1007/s12105-016-0725-6
Intraoral Pseudo-Onion Bulb Intraneural Proliferations in a Patient with Hemimandibular Hyperplasia: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
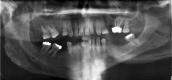
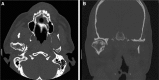
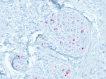
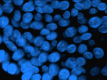
This report and review of the literature describes a case of benign intraoral lesions of perineurial origin in a patient with symptomatic hemimandibular hyperplasia causing partial denture soreness. Perineuriomas are a benign peripheral nerve sheath tumor composed of perineurial cells. Intraoral perineuriomas are an extremely rare entity. Two main types of perineuriomas have been described: intraneural and extraneural perineuriomas. A third, similar entity, called an intraneural pseudoperineuriomatous proliferation, has recently been proposed in the literature as a separate and distinctive diagnosis. This report describes the histologic and clinical presentation of intraneural pseudoperineuriomatous proliferations in a patient with hemimandibular hyperplasia.
Keywords: Fluorescence in situ hybridization; Hemimandibular hyperplasia; Immunohistochemistry; Intraneural pseudoperineuriomatous proliferation; Oral pathology; Perineurioma.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Multiple orofacial intraneural perineuriomas in a patient with hemifacial hyperplasia.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007 Jul;104(1):e38-44. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2006.12.030. Epub 2007 Apr 23. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007. PMID: 17449293
-
On pseudo-onion bulb intraneural proliferations of the non-major nerves of the oral mucosa.Head Neck Pathol. 2013 Dec;7(4):334-43. doi: 10.1007/s12105-013-0446-z. Epub 2013 May 5. Head Neck Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23645379 Free PMC article.
-
Cutaneous intraneural perineurioma: a case report.Am J Dermatopathol. 2013 May;35(3):e45-8. doi: 10.1097/DAD.0b013e31827747d6. Am J Dermatopathol. 2013. PMID: 23221470
-
Intraneural malignant perineurioma: a case report and review of literature.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Jun 15;7(7):4503-7. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25120842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Can Intraneural Perineuriomas Occur Intradurally? An Anatomic Perspective.Neurosurgery. 2017 Feb 1;80(2):226-234. doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyw028. Neurosurgery. 2017. PMID: 28173435 Review.
Cited by
-
Intraneural Pseudoperineuriomatous Proliferations and Traumatic Neuromas: A Retrospective Multicenter Study of Clinicopathological Characteristics.Head Neck Pathol. 2025 Mar 15;19(1):32. doi: 10.1007/s12105-025-01771-5. Head Neck Pathol. 2025. PMID: 40088303
-
Orofacial overgrowth with peripheral nerve enlargement and perineuriomatous pseudo-onion bulb proliferations is part of the PIK3CA-related overgrowth spectrum.HGG Adv. 2020 Aug 14;1(1):100009. doi: 10.1016/j.xhgg.2020.100009. eCollection 2020 Oct 22. HGG Adv. 2020. PMID: 35047831 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boyanton BL, Jr, Jones JK, Shenaq SM, Hicks MJ, Bhattacharjee MB. Intraneural perineurioma: a systematic review with illustrative cases. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2007;131(9):1382–1392. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

