TGF-β and the TGF-β Family: Context-Dependent Roles in Cell and Tissue Physiology
- PMID: 27141051
- PMCID: PMC4852809
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a021873
TGF-β and the TGF-β Family: Context-Dependent Roles in Cell and Tissue Physiology
Abstract
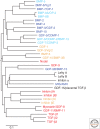
The transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) is the prototype of the TGF-β family of growth and differentiation factors, which is encoded by 33 genes in mammals and comprises homo- and heterodimers. This review introduces the reader to the TGF-β family with its complexity of names and biological activities. It also introduces TGF-β as the best-studied factor among the TGF-β family proteins, with its diversity of roles in the control of cell proliferation and differentiation, wound healing and immune system, and its key roles in pathology, for example, skeletal diseases, fibrosis, and cancer.
Copyright © 2016 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Amendt C, Mann A, Schirmacher P, Blessing M. 2002. Resistance of keratinocytes to TGFβ-mediated growth restriction and apoptosis induction accelerates re-epithelialization in skin wounds. J Cell Sci 115: 2189–2198. - PubMed
-
- Anido J, Saez-Borderias A, Gonzalez-Junca A, Rodon L, Folch G, Carmona MA, Prieto-Sanchez RM, Barba I, Martinez-Saez E, Prudkin L, et al. 2010. TGF-β receptor inhibitors target the CD44high/Id1high glioma-initiating cell population in human glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 18: 655–668. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
