Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor-Dependent and -Independent Paracrine Signaling by Sunitinib-Resistant Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 27141054
- PMCID: PMC4911743
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00189-16
Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor-Dependent and -Independent Paracrine Signaling by Sunitinib-Resistant Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
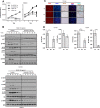
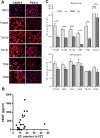
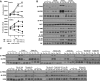
Antiangiogenic therapies, such as sunitinib, have revolutionized renal cell carcinoma (RCC) treatment. However, a precarious understanding of how resistance emerges and a lack of tractable experimental systems hinder progress. We evaluated the potential of primary RCC cultures (derived from tumors and tumor grafts) to signal to endothelial cells (EC) and fibroblasts in vitro and to stimulate angiogenesis ex vivo in chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assays. From 65 patients, 27 primary cultures, including several from patients with sunitinib-resistant RCC, were established. RCC cells supported EC survival in coculture assays and induced angiogenesis in CAM assays. RCC-induced EC survival was sensitive to sunitinib in half of the tumors and was refractory in tumors from resistant patients. Sunitinib sensitivity correlated with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) production. RCC induced paracrine extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation in EC which was inhibited by sunitinib in sensitive but not in resistant tumors. As determined by fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2 (FRS2) phosphorylation in fibroblasts, RCC broadly induced low-level fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) signaling. Whereas ERK activation in EC was uniformly inhibited by combined VEGF/platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)/FGF receptor inhibitors, paracrine ERK activation in fibroblasts was blocked in only a fraction of tumors. Our data show that RCC activates EC through VEGF-dependent and -independent pathways, that sunitinib sensitivity correlates with VEGF-mediated ERK activation, and that combined inhibition of VEGF/PDGF/FGF receptors is sufficient to inhibit mitogenic signaling in EC but not in fibroblasts.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



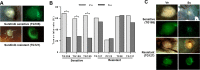



Similar articles
-
Cellular Adaptation to VEGF-Targeted Antiangiogenic Therapy Induces Evasive Resistance by Overproduction of Alternative Endothelial Cell Growth Factors in Renal Cell Carcinoma.Neoplasia. 2015 Nov;17(11):805-16. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2015.11.001. Neoplasia. 2015. PMID: 26678908 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenomedullin blockade suppresses sunitinib-resistant renal cell carcinoma growth by targeting the ERK/MAPK pathway.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 27;7(39):63374-63387. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11463. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27556517 Free PMC article.
-
Autotaxin-lysophosphatidic acid signaling axis mediates tumorigenesis and development of acquired resistance to sunitinib in renal cell carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Dec 1;19(23):6461-72. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1284. Epub 2013 Oct 11. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24122794 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of fibroblast growth factor receptor in neovascularization and tumor escape from antiangiogenic therapy.Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2012 Jun;10(2):77-83. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2012.01.010. Epub 2012 Feb 28. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22382009 Review.
-
Sunitinib, sorafenib and mTOR inhibitors in renal cancer.J BUON. 2007 Sep;12 Suppl 1:S151-62. J BUON. 2007. PMID: 17935273 Review.
Cited by
-
Microphysiological model of renal cell carcinoma to inform anti-angiogenic therapy.Biomaterials. 2022 Apr;283:121454. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121454. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Biomaterials. 2022. PMID: 35299086 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin Inhibits Proliferation of Renal Cell Carcinoma in vitro and in vivo by Regulating miR-148/ADAMTS18 through Suppressing Autophagy.Chin J Integr Med. 2023 Aug;29(8):699-706. doi: 10.1007/s11655-022-3690-9. Epub 2022 Dec 7. Chin J Integr Med. 2023. PMID: 36477451
-
Hsa_circ_0072732 enhances sunitinib resistance of renal cell carcinoma by inhibiting ferroptosis.Discov Oncol. 2024 Nov 23;15(1):700. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01580-2. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39580569 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin reverses the sunitinib resistance in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) through the induction of ferroptosis via the ADAMTS18 gene.Transl Cancer Res. 2021 Jul;10(7):3158-3167. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-227. Transl Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35116623 Free PMC article.
-
Update on Circulating Tumor Cells in Genitourinary Tumors with Focus on Prostate Cancer.Cells. 2020 Jun 19;9(6):1495. doi: 10.3390/cells9061495. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32575429 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nickerson ML, Jaeger E, Shi Y, Durocher JA, Mahurkar S, Zaridze D, Matveev V, Janout V, Kollarova H, Bencko V, Navratilova M, Szeszenia-Dabrowska N, Mates D, Mukeria A, Holcatova I, Schmidt LS, Toro JR, Karami S, Hung R, Gerard GF, Linehan WM, Merino M, Zbar B, Boffetta P, Brennan P, Rothman N, Chow WH, Waldman FM, Moore LE. 2008. Improved identification of von Hippel-Lindau gene alterations in clear cell renal tumors. Clin Cancer Res 14:4726–4734. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4921. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
