Assessing Vocal Development in Infants and Toddlers Who Are Hard of Hearing: A Parent-Report Tool
- PMID: 27141092
- PMCID: PMC4902879
- DOI: 10.1093/deafed/enw027
Assessing Vocal Development in Infants and Toddlers Who Are Hard of Hearing: A Parent-Report Tool
Abstract
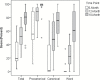
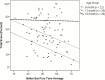
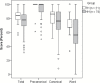
The main purpose of the current investigation was to determine whether the Vocal Development Landmarks Interview-Experimental Version (VDLI-E) was sensitive to variation in the vocal development of infants and toddlers who are hard of hearing. The VDLI-E is an interactive parent interview that uses audio samples of authentic infant vocalizations to make targeted vocal behaviors clear and understandable to parents without the need for technical terms, verbal descriptions, or adult modeling of infant productions. The VDLI-E was found to be sensitive to age and hearing and was related to performance on concurrent measures of early auditory skills, expressive vocabulary, and overall expressive language abilities. These findings provide preliminary support for the utility of this measure in monitoring the impact of early auditory experiences on vocal development for 6- to 18-month-old children who are hard of hearing.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- ANSI (1997). Methods for calculation of the speech intelligibility index. Technical Report S3.5-1997. New York, NY: American National Standards Institute.
-
- Bates E. Bretherton I., & Snyder L (1991). From first words to grammar: Individual differences and dissociable mechanisms. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
-
- Bates E. Dale P. S., & Thal D (1995). Individual differences and their implications for theories of language development. In Fletcher P., MacWhinney B. (Eds.), The handbook of child language (pp. 96–151). Oxford, UK: Blackwell.
-
- Ben-Itzhak D., Greenstein T., Kishon-Rabin L. (2014). Parent report of the development of auditory skills in infants and toddlers who use hearing aids. Ear and Hearing, 35, e262–e271. doi:10.1097/AUD.0000000000000059 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

