Solitary pulmonary nodule and (18)F-FDG PET/CT. Part 2: accuracy, cost-effectiveness, and current recommendations
- PMID: 27141133
- PMCID: PMC4851481
- DOI: 10.1590/0100-3984.2014.0087
Solitary pulmonary nodule and (18)F-FDG PET/CT. Part 2: accuracy, cost-effectiveness, and current recommendations
Abstract
A solitary pulmonary nodule is a common, often incidental, radiographic finding. The investigation and differential diagnosis of solitary pulmonary nodules remain complex, because there are overlaps between the characteristics of benign and malignant processes. There are currently many strategies for evaluating solitary pulmonary nodules. The main objective is to identify benign lesions, in order to avoid exposing patients to the risks of invasive methods, and to detect cases of lung cancer accurately, in order to avoid delaying potentially curative treatment. The focus of this study was to review the evaluation of solitary pulmonary nodules, to discuss the current role of (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography, addressing its accuracy and cost-effectiveness, and to detail the current recommendations for the examination in this scenario.
O nódulo pulmonar solitário corresponde a um achado radiológico comum, cuja detecção ocorre frequentemente de forma incidental. A investigação desta entidade permanece complexa, uma vez que existem sobreposições entre as características dos processos benignos e malignos no seu diagnóstico diferencial. Atualmente, muitas estratégias estão disponíveis para a avaliação do nódulo pulmonar solitário, e o objetivo principal consiste em caracterizar da melhor forma possível as alterações benignas, não expondo os pacientes aos riscos de métodos invasivos, e detectar corretamente os casos de câncer de pulmão, não retardando potencial tratamento curativo. O foco deste estudo é revisar a avaliação do nódulo pulmonar solitário, discutindo o papel atual da tomografia por emissão de pósitrons com 18-fluordesoxiglicose, apresentar sua acurácia e custo-efetividade, bem como salientar as recomendações atuais do exame neste cenário.
Keywords: Positron-emission tomography; Solitary pulmonary nodule.
Figures
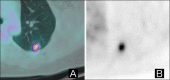

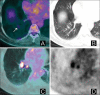
References
-
- Gould MK, Maclean CC, Kuschner WG, et al. Accuracy of positron emission tomography for diagnosis of pulmonary nodules and mass lesions: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2001;285:914–924. - PubMed
-
- Fletcher JW, Kymes SM, Gould MK, et al. A comparison of the diagnostic accuracy of 18F-FDG PET and CT in the characterization of solitary pulmonary nodules. J Nucl Med. 2008;49:179–185. - PubMed
-
- Grgic A, Yüksel Y, Gröschel A, et al. Risk stratification of solitary pulmonary nodules by means of PET using (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose and SUV quantification. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37:1087–1094. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto Y, Tsujikawa T, Kondo C, et al. Accuracy of PET for diagnosis of solid pulmonary lesions with 18F-FDG uptake below the standardized uptake value of 2.5. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:426–431. - PubMed
-
- Herder GJ, Golding RP, Hoekstra OS, et al. The performance of (18)F-fluorodeoxiglucose positron emission tomography in small solitary pulmonary nodules. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2004;31:1231–1236. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
