Effect of Thymoquinone on P53 Gene Expression and Consequence Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Cell Line
- PMID: 27141285
- PMCID: PMC4837800
- DOI: 10.4103/2008-7802.180412
Effect of Thymoquinone on P53 Gene Expression and Consequence Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Cell Line
Abstract
Background: Nigella sativa has been a nutritional flavoring factor and natural treatment for many ailments for so many years in medical science. Earlier studies have been reported that thymoquinone (TQ), an active compound of its seed, contains anticancer properties. Previous studies have shown that TQ induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells but it is unclear the role of P53 in the apoptotic pathway. Hereby, this study reports the potency of TQ on expression of tumor suppressor gene P53 and apoptosis induction in breast cancer cell line Michigan Cancer Foundation-7 (MCF-7).
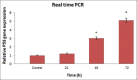
Methods: MCF-7 cell line was cultured and treated with TQ, and 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay was carried out for evaluating the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values after 24 h of treatment. The percentage of apoptotic cells was measured by flow cytometry. Real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed to estimate the messenger RNA expression of P53 in MCF-7 cell line at different times.
Results: The IC50 value for the TQ in MCF-7 cells was 25 μM that determined using MTT assay. The flow cytometry and real-time PCR results showed that TQ could induce apoptosis in MCF-7 cells, and the P53 gene expression was dramatically up-regulated by ascending time, respectively. Hence, there was significant difference in 48 and 72 h.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrated that TQ could induce apoptosis in MCF-7 cells through up-regulation of P53 expression in breast cancer cell line (MCF-7) by time-dependent manner.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Michigan C]ancer Foundation-7 cells; genes P53; thymoquinone.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

