Quantitative analysis of nanoparticle transport through in vitro blood-brain barrier models
- PMID: 27141425
- PMCID: PMC4836482
- DOI: 10.1080/21688370.2016.1143545
Quantitative analysis of nanoparticle transport through in vitro blood-brain barrier models
Abstract
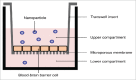
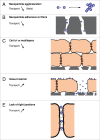
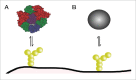
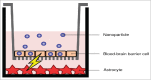
Nanoparticle transport through the blood-brain barrier has received much attention of late, both from the point of view of nano-enabled drug delivery, as well as due to concerns about unintended exposure of nanomaterials to humans and other organisms. In vitro models play a lead role in efforts to understand the extent of transport through the blood-brain barrier, but unique features of the nanoscale challenge their direct adaptation. Here we highlight some of the differences compared to molecular species when utilizing in vitro blood-brain barrier models for nanoparticle studies. Issues that may arise with transwell systems are discussed, together with some potential alternative methodologies. We also briefly review the biomolecular corona concept and its importance for how nanoparticles interact with the blood-brain barrier. We end with considering future directions, including indirect effects and application of shear and fluidics-technologies.
Keywords: biomolecular corona; blood-brain barrier; nanomedicine; nanoparticles; nanosafety; transwell systems.
Figures
References
-
- Sanhai WR, Sakamoto JH, Canady R, Ferrari M. Seven challenges for nanomedicine. Nat Nanotechnol 2008; 3:242-4; PMID:18654511; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2008.114 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Farokhzad OC, Langer R. Impact of nanotechnology on drug delivery. ACS Nano 2009; 3:16-20; PMID:19206243; http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn90-0002m - DOI - PubMed
-
- Moghimi SM, Hunter AC, Murray JC. Nanomedicine: Current status and future prospects. FASEB J 2005; 19:311-30; PMID:15746175; http://dx.doi.org/10.1096/fj.04-2747rev - DOI - PubMed
-
- Couvreur P. Nanoparticles in drug delivery: Past, present and future. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2013; 65:21-3; PMID:22580334; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2012.04.010 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fang J, Nakamura H, Maeda H. The EPR effect: Unique features of tumor blood vessels for drug delivery, factors involved, and limitations and augmentation of the effect. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2011; 63:136-51; PMID:20441782; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2010.04.009 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
