Cloning, expression and characterization of a β-D-xylosidase from Lactobacillus rossiae DSM 15814(T)
- PMID: 27142164
- PMCID: PMC4855831
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-016-0473-z
Cloning, expression and characterization of a β-D-xylosidase from Lactobacillus rossiae DSM 15814(T)
Abstract
Background: Among the oligosaccharides that may positively affect the gut microbiota, xylo-oligosaccharides (XOS) and arabinoxylan oligosaccharides (AXOS) possess promising functional properties. Ingestion of XOS has been reported to contribute to anti-oxidant, anti-bacterial, immune-modulatory and anti-diabetic activities. Because of the structural complexity and chemical heterogeneity, complete degradation of xylan-containing plant polymers requires the synergistic activity of several enzymes. Endo-xylanases and β-D-xylosidases, collectively termed xylanases, represent the two key enzymes responsible for the sequential hydrolysis of xylan. Xylanase cocktails are used on an industrial scale for biotechnological purposes. Lactobacillus rossiae DSM 15814(T) can utilize an extensive set of carbon sources, an ability that is likely to contribute to its adaptive ability. In this study, the capacity of this strain to utilize XOS, xylan, D-xylose and L-arabinose was investigated.
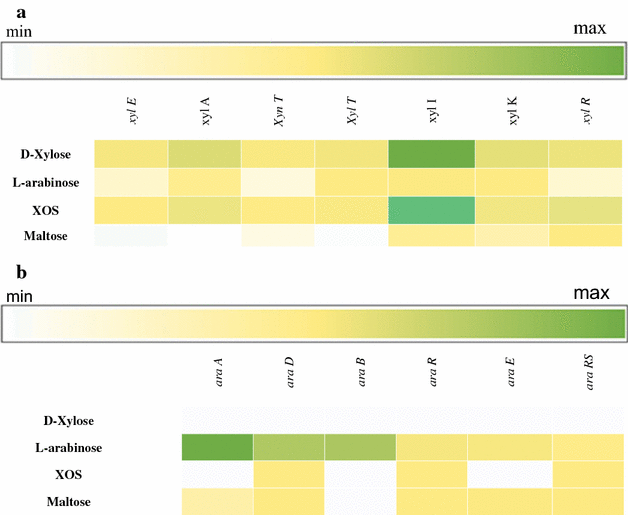
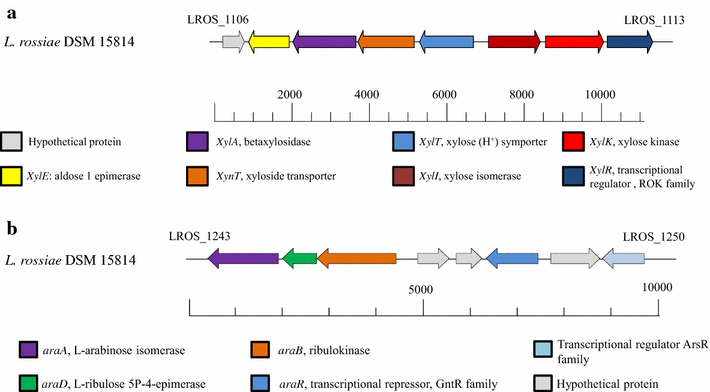
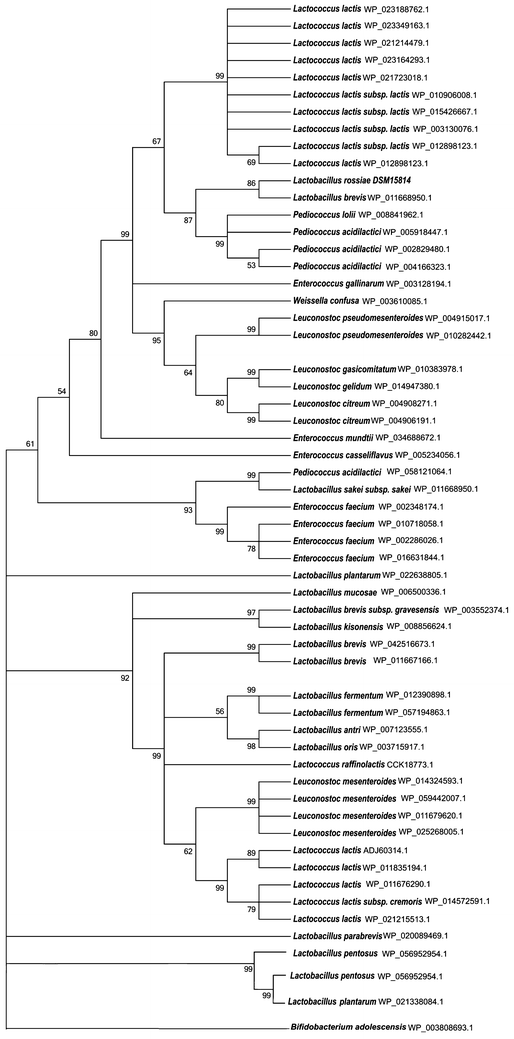
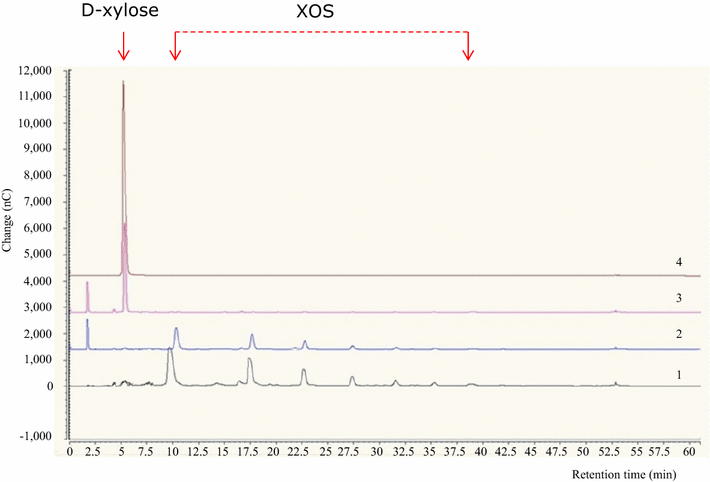
Results: Genomic and transcriptomic analyses revealed the presence of two gene clusters, designated xyl and ara, encoding proteins predicted to be responsible for XOS uptake and hydrolysis and D-xylose utilization, and L-arabinose metabolism, respectively. The deduced amino acid sequence of one of the genes of the xyl gene cluster, LROS_1108 (designated here as xylA), shows high similarity to (predicted) β-D-xylosidases encoded by various lactic acid bacteria, and belongs to glycosyl hydrolase family 43. Heterologously expressed XylA was shown to completely hydrolyse XOS to xylose and showed optimal activity at pH 6.0 and 40 °C. Furthermore, β-D-xylosidase activity of L. rossiae DSM 15814(T) was also measured under sourdough conditions.
Conclusions: This study highlights the ability of L. rossiae DSM 15814(T) to utilize XOS, which is a very useful trait when selecting starters with specific metabolic performances for sourdough fermentation or as probiotics.
Keywords: Functional foods; Gut microbiota; Prebiotic; Probiotic; Sourdough; Xylo-oligosaccharides.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enzymatic hydrolysis of wheat arabinoxylan by a recombinant "minimal" enzyme cocktail containing beta-xylosidase and novel endo-1,4-beta-xylanase and alpha-l-arabinofuranosidase activities.Biotechnol Prog. 2007 Jan-Feb;23(1):100-7. doi: 10.1021/bp0601701. Biotechnol Prog. 2007. PMID: 17269676
-
Characterization of the arabinoxylan-degrading machinery of the thermophilic bacterium Herbinix hemicellulosilytica-Six new xylanases, three arabinofuranosidases and one xylosidase.J Biotechnol. 2017 Sep 10;257:122-130. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.04.023. Epub 2017 Apr 25. J Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28450260
-
Highly thermostable GH39 β-xylosidase from a Geobacillus sp. strain WSUCF1.BMC Biotechnol. 2014 Dec 23;14:963. doi: 10.1186/s12896-014-0106-8. BMC Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25532585 Free PMC article.
-
A mini review of xylanolytic enzymes with regards to their synergistic interactions during hetero-xylan degradation.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Nov 14;35(12):187. doi: 10.1007/s11274-019-2765-z. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31728656 Review.
-
Properties and applications of microbial beta-D-xylosidases featuring the catalytically efficient enzyme from Selenomonas ruminantium.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010 May;86(6):1647-58. doi: 10.1007/s00253-010-2538-y. Epub 2010 Mar 30. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20352422 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of Zalaria obscura Y1223 hydrolases: implications for lignocellulose conversion.AMB Express. 2025 Jul 23;15(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s13568-025-01907-4. AMB Express. 2025. PMID: 40699489 Free PMC article.
-
Draft Genome Sequence of Lactobacillus reuteri 121, a Source of α-Glucan and β-Fructan Exopolysaccharides.Genome Announc. 2017 Mar 9;5(10):e01691-16. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.01691-16. Genome Announc. 2017. PMID: 28280024 Free PMC article.
-
Degradation of beechwood xylan using food-grade bacteria-like particles displaying β-xylosidase from Limosilactobacillus fermentum.Bioresour Bioprocess. 2025 Jun 19;12(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s40643-025-00898-1. Bioresour Bioprocess. 2025. PMID: 40536589 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the bifidogenic and antibacterial activities of xylooligosaccharide.Front Nutr. 2022 Aug 25;9:858949. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.858949. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36091239 Free PMC article.
-
Shifts in xylanases and the microbial community associated with xylan biodegradation during treatment with rumen fluid.Microb Biotechnol. 2022 Jun;15(6):1729-1743. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13988. Epub 2021 Dec 28. Microb Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34964273 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Younes H, Garleb K, Behr S, Remesy C, Demigne C. Fermentable fibers or oligosaccharides reduce urinary nitroben excretion by increasing urea disposal in the rat cecum. J Nutr. 1995;125:1010–1016. - PubMed
-
- McLaughlin HP, Motherway MO, Lakshminarayanan B, Stanton C, Paul Ross R, Brulc J, Menon R, O’Toole PW, van Sinderen D. Carbohydrate catabolic diversity of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli of human origin. Int J Food Microbiol. 2015 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

