Integrated analysis of miRNA and mRNA expression profiles in tilapia gonads at an early stage of sex differentiation
- PMID: 27142172
- PMCID: PMC4855716
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-016-2636-z
Integrated analysis of miRNA and mRNA expression profiles in tilapia gonads at an early stage of sex differentiation
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) represent a second regulatory network that has important effects on gene expression and protein translation during biological process. However, the possible role of miRNAs in the early stages of fish sex differentiation is not well understood. In this study, we carried an integrated analysis of miRNA and mRNA expression profiles to explore their possibly regulatory patterns at the critical stage of sex differentiation in tilapia.
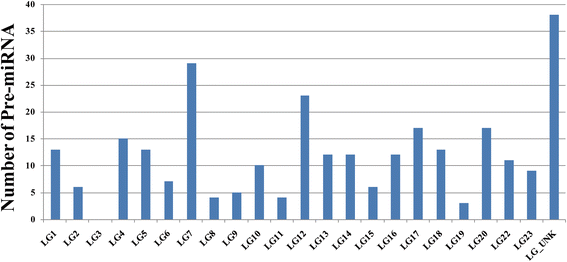
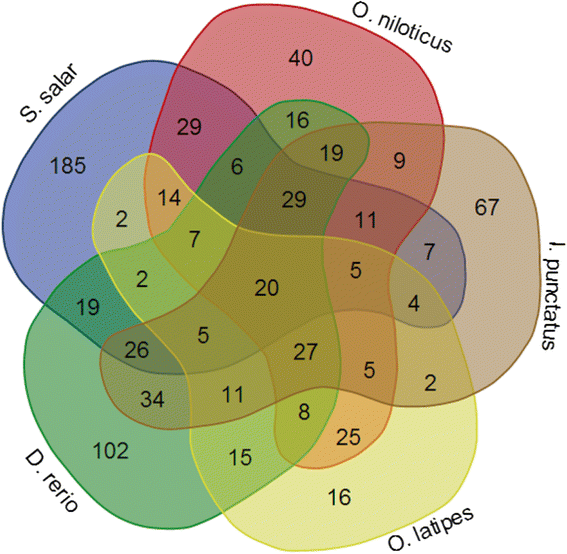
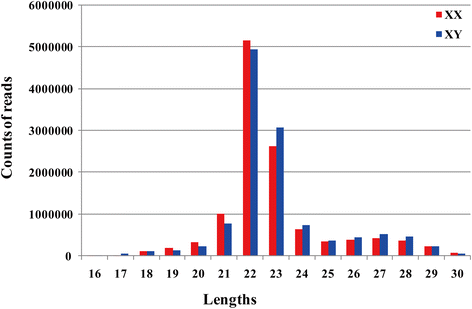
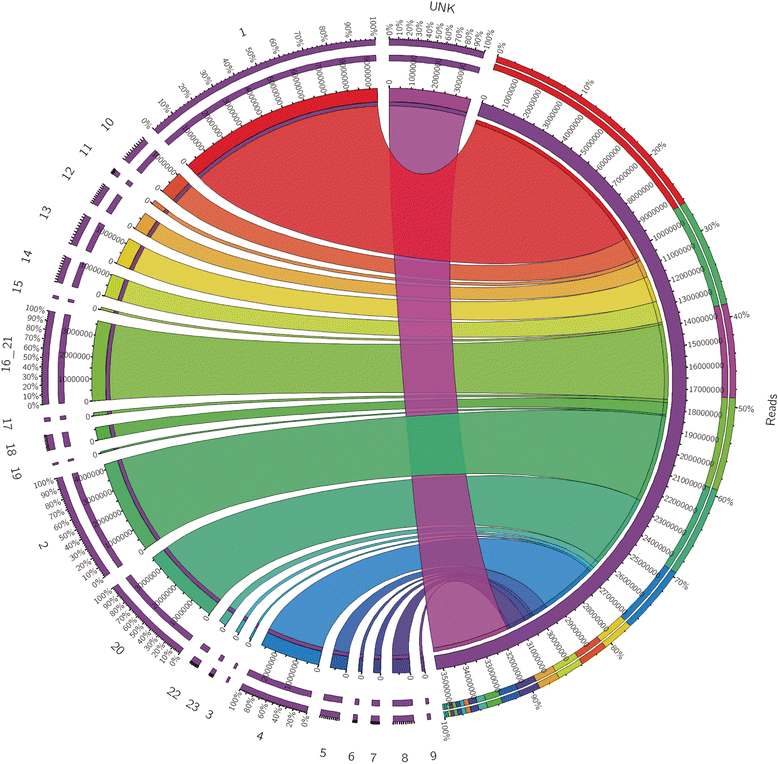
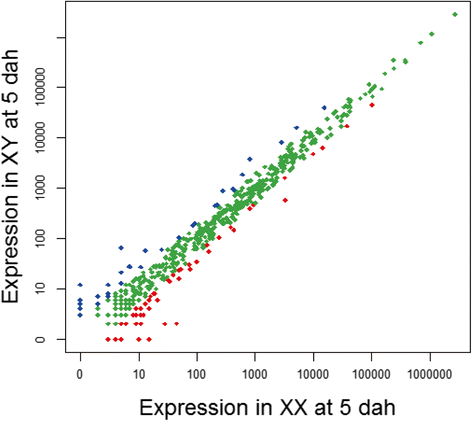
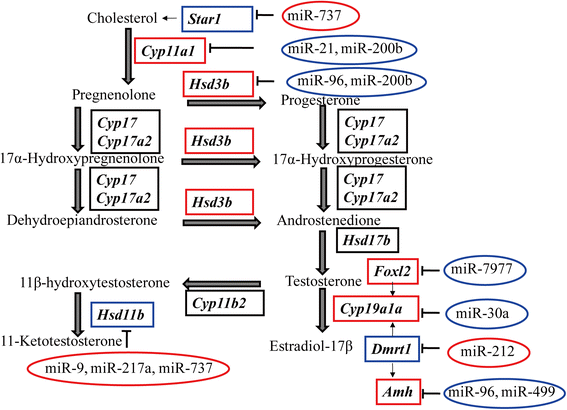
Results: We identified 279 pre-miRNA genes in tilapia genome, which were highly conserved in other fish species. Based on small RNA library sequencing, we identified 635 mature miRNAs in tilapia gonads, in which 62 and 49 miRNAs showed higher expression in XX and XY gonads, respectively. The predicted targets of these sex-biased miRNAs (e.g., miR-9, miR-21, miR-30a, miR-96, miR-200b, miR-212 and miR-7977) included genes encoding key enzymes in steroidogenic pathways (Cyp11a1, Hsd3b, Cyp19a1a, Hsd11b) and key molecules involved in vertebrate sex differentiation (Foxl2, Amh, Star1, Sf1, Dmrt1, and Gsdf). These genes also showed sex-biased expression in tilapia gonads at 5 dah. Some miRNAs (e.g., miR-96 and miR-737) targeted multiple genes involved in steroid synthesis, suggesting a complex miRNA regulatory network during early sex differentiation in this fish.
Conclusions: The sequence and expression patterns of most miRNAs in tilapia are conserved in fishes, indicating the basic functions of vertebrate miRNAs might share a common evolutionary origin. This comprehensive analysis of miRNA and mRNA at the early stage of molecular sex differentiation in tilapia XX and XY gonads lead to the discovery of differentially expressed miRNAs and their putative targets, which will facilitate studies of the regulatory network of molecular sex determination and differentiation in fishes.
Keywords: Early sex differentiation; Tilapia; mRNA; miRNA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Coordinated microRNA and messenger RNA expression profiles for understanding sexual dimorphism of gonads and the potential roles of microRNA in the steroidogenesis pathway in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus).Theriogenology. 2016 Mar 15;85(5):970-978. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2015.11.006. Epub 2015 Nov 19. Theriogenology. 2016. PMID: 26719037
-
Sexual dimorphic expression of genes in gonads during early differentiation of a teleost fish, the Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus.Biol Reprod. 2008 Feb;78(2):333-41. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.107.064246. Epub 2007 Oct 17. Biol Reprod. 2008. PMID: 17942796
-
Identification and profiling of Cyprinus carpio microRNAs during ovary differentiation by deep sequencing.BMC Genomics. 2017 Apr 28;18(1):333. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3701-y. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28454515 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of miRNA-mRNA expression in the brain during high temperature-induced masculinization of female Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus).Genomics. 2024 May;116(3):110856. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2024.110856. Epub 2024 May 10. Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38734154 Review.
-
Tilapia, a good model for studying reproductive endocrinology.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2024 Jan 1;345:114395. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2023.114395. Epub 2023 Oct 23. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 37879418 Review.
Cited by
-
microRNA-mRNA Analysis Reveals Tissue-Specific Regulation of microRNA in Mangrove Clam (Geloina erosa).Biology (Basel). 2023 Dec 11;12(12):1510. doi: 10.3390/biology12121510. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38132336 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering sex-specific miRNAs as heat-recorders in zebrafish.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 4;12(1):18722. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-21864-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36333360 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Comparison of microRNAs in the Gonad of the Yellowfin Seabream (Acanthopagrus Latus).Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 8;21(16):5690. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165690. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32784462 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual Antagonism and Sex Determination in Three Syngnathid Species Alongside a Male Pregnancy Gradient.Genome Biol Evol. 2025 Jul 3;17(7):evaf103. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evaf103. Genome Biol Evol. 2025. PMID: 40619149 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated mRNA and miRNA Expression Profile Analysis of Female and Male Gonads in Acrossocheilus fasciatus.Biology (Basel). 2022 Aug 31;11(9):1296. doi: 10.3390/biology11091296. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36138775 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

