Effects of neurostimulation for advanced Parkinson's disease patients on motor symptoms: A multiple-treatments meta-analysas of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 27142183
- PMCID: PMC4855136
- DOI: 10.1038/srep25285
Effects of neurostimulation for advanced Parkinson's disease patients on motor symptoms: A multiple-treatments meta-analysas of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is the surgical procedure of choice for patients with advanced Parkinson disease (PD). We aim to evaluate the efficacy of GPi (globus pallidus internus), STN (subthalamic nucleus)-DBS and medical therapy for PD. We conducted a systematic review and multiple-treatments meta-analysis to investigate the efficacy of neurostimulation and medical therapy for PD patients. Sixteen eligible studies were included in this analysis. We pooled the whole data and found obvious difference between GPi-DBS versus medical therapy and STN-DBS versus medical therapy in terms of UPDRS scores (Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale). Meanwhile, we found GPi-DBS had the similar efficacy on the UPDRS scores when compared with STN-DBS. What is more, quality of life, measured by PDQ-39 (Parkinson's disease Questionnaire) showed greater improvement after GPi-DBS than STN-DBS. Five studies showed STN-DBS was more effective for reduction in medication than GPi-DBS. Overall, either GPi-DBS or STN-DBS was an effective technique to control PD patients' symptoms and improved their functionality and quality of life. Meanwhile, the UPDRS scores measuring parkinsonian symptoms revealed no significant difference between GPi-DBS and STN-DBS. STN-DBS was more effective for reduction in medication than GPi-DBS. Alternatively, GPi-DBS was more effective for improving the PDQ-39 score than STN-DBS.
Figures
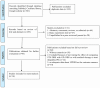
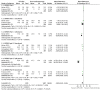

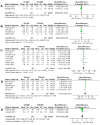


References
-
- Vidailhet M. Movement disorders in 2010: Parkinson disease-symptoms and treatments. Nat Rev Neurol 7, 70–72 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Jankovic J. & Sherer T. The future of research in Parkinson disease. JAMA Neurol 71, 1351–1352 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Velseboer D. C. et al. Prognostic factors of motor impairment, disability, and quality of life in newly diagnosed PD. Neurology 8, 627–633 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Malkki H. Parkinson disease: deep brain stimulation might alleviate parkinsonism by reducing excessive synchronization in primary motor cortex. Nat Rev Neurol 11, 246 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Li Q., Qian Z. M., Arbuthnott G. W., Ke Y. & Yung W. H. Cortical effects of deep brain stimulation: implications for pathogenesis and treatment of Parkinson disease. JAMA Neurol 71, 100–103 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

