CPEB1 restrains proliferation of Glioblastoma cells through the regulation of p27(Kip1) mRNA translation
- PMID: 27142352
- PMCID: PMC4855225
- DOI: 10.1038/srep25219
CPEB1 restrains proliferation of Glioblastoma cells through the regulation of p27(Kip1) mRNA translation
Abstract
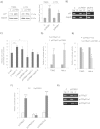
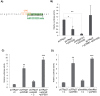
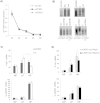
The cytoplasmic element binding protein 1 (CPEB1) regulates many important biological processes ranging from cell cycle control to learning and memory formation, by controlling mRNA translation efficiency via 3' untranslated regions (3'UTR). In the present study, we show that CPEB1 is significantly downregulated in human Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM) tissues and that the restoration of its expression impairs glioma cell lines growth. We demonstrate that CPEB1 promotes the expression of the cell cycle inhibitor p27(Kip1) by specifically targeting its 3'UTR, and competes with miR-221/222 binding at an overlapping site in the 3'UTR, thus impairing miR-221/222 inhibitory activity. Upon binding to p27(Kip1) 3'UTR, CPEB1 promotes elongation of poly-A tail and the subsequent translation of p27(Kip1) mRNA. This leads to higher levels of p27(Kip1) in the cell, in turn significantly inhibiting cell proliferation, and confers to CPEB1 a potential value as a tumor suppressor in Glioblastoma.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Roles of Cytoplasmic Polyadenylation Element Binding Protein 1 in Tumorigenesis.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024;24(22):2008-2018. doi: 10.2174/0113895575293544240605112838. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38879767 Review.
-
CPEB1 regulates the expression of MTDH/AEG-1 and glioblastoma cell migration.Mol Cancer Res. 2013 Feb;11(2):149-60. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-12-0498. Epub 2013 Jan 29. Mol Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23360795
-
Regulation of p27Kip1 by miRNA 221/222 in glioblastoma.Cell Cycle. 2007 Aug 15;6(16):2005-9. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.16.4526. Epub 2007 May 31. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17721077
-
PCBP1 depletion promotes tumorigenesis through attenuation of p27Kip1 mRNA stability and translation.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Aug 7;37(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0840-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30086790 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic Polyadenylation Element Binding Protein 1 and Atherosclerosis: Prospective Target and New Insights.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2024;22(2):95-105. doi: 10.2174/0115701611258090231221082502. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38284693 Review.
Cited by
-
The regulatory role of microRNAs in angiogenesis-related diseases.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Oct;22(10):4568-4587. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13700. Epub 2018 Jun 29. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29956461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A narrative review of papillary thyroid carcinoma-related long non-coding RNAs and their relevance to malignant tumors.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Mar 30;14(3):2125-2149. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-1038. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40224997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CPEB1 mediates hepatocellular carcinoma cancer stemness and chemoresistance.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Sep 20;9(10):957. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0974-2. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30237545 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor suppressor role of cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein 2 (CPEB2) in human mammary epithelial cells.BMC Cancer. 2019 Jun 11;19(1):561. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5771-5. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31185986 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of Cytoplasmic Polyadenylation Element Binding Protein 1 in Tumorigenesis.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024;24(22):2008-2018. doi: 10.2174/0113895575293544240605112838. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38879767 Review.
References
-
- Mendez R. & Richter J. D. Traslational control by CPEB: a means to the end. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2, 521–529 (2001) - PubMed
-
- Richter J. D. CPEB: a life in translation. Trends Biochem Sci. 32, 279–85 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Weill L., Belloc E., Bava F. A. & Mendez R. Translational control by changes in poly(A) tail length: recycling mRNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 19, 577–585 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Groisman I. et al. CPEB, maskin, and cyclin B1 mRNA at the mitotic apparatus: implications for local translational control of cell division. Cell. 103, 435–447 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

