Comparison of the non-invasive Nexfin® monitor with conventional methods for the measurement of arterial blood pressure in moderate risk orthopaedic surgery patients
- PMID: 27142436
- PMCID: PMC5536626
- DOI: 10.1177/0300060516635383
Comparison of the non-invasive Nexfin® monitor with conventional methods for the measurement of arterial blood pressure in moderate risk orthopaedic surgery patients
Abstract
Objective: Continuous invasive arterial blood pressure (IBP) monitoring remains the gold standard for BP measurement, but traditional oscillometric non-invasive intermittent pressure (NIBP) measurement is used in most low-to-moderate risk procedures. This study compared non-invasive continuous arterial BP measurement using a Nexfin® monitor with NIBP and IBP monitors.
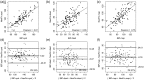
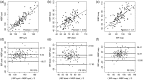
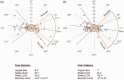
Methods: This was a single-centre, prospective, pilot study in patients scheduled for elective orthopaedic surgery. Systolic BP, diastolic BP and mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) were measured by Nexfin®, IBP and NIBP at five intraoperative time-points. Pearson correlation coefficients, Bland-Altman plots and trending ability of Nexfin® measurements were used as criteria for success in the investigation of measurement reliability.
Results: A total of 20 patients were enrolled in the study. For MAP, there was a sufficient correlation between IBP/Nexfin® (Pearson = 0.75), which was better than the correlation between IBP/NIBP (Pearson = 0.70). Bland-Altman analysis of the data showed that compared with IBP, there was a higher percentage error for MAPNIBP (30%) compared with MAPNexfin® (27%). Nexfin® and NIBP underestimated systolic BP; NIBP also underestimated diastolic BP and MAP. Trending ability for MAPNexfin® and MAPNIBP were comparable to IBP.
Conclusion: Non-invasive BP measurement with Nexfin® was comparable with IBP and tended to be more precise than NIBP.
Keywords: Blood pressure; Nexfin® Trial registration: ClinGov. NCT01263990; invasive arterial pressure; monitoring; non-invasive arterial pressure.
© The Author(s) 2016.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of oscillometric, non-invasive and invasive arterial pressure monitoring in patients undergoing laparoscopic bariatric surgery - a secondary analysis of a prospective observational study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2022 Mar 28;22(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12871-022-01619-3. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022. PMID: 35346046 Free PMC article.
-
Oscillometric and intra-arterial blood pressure in children post-kidney transplantation: Is invasive blood pressure measurement always needed?Pediatr Transplant. 2019 Feb;23(1):e13309. doi: 10.1111/petr.13309. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Pediatr Transplant. 2019. PMID: 30362265
-
Level of agreement between Nexfin non-invasive arterial pressure with invasive arterial pressure measurements in children.Br J Anaesth. 2012 Oct;109(4):609-15. doi: 10.1093/bja/aes295. Epub 2012 Aug 19. Br J Anaesth. 2012. PMID: 22907342
-
Noninvasive BP Monitoring in the Critically Ill: Time to Abandon the Arterial Catheter?Chest. 2018 Apr;153(4):1023-1039. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2017.10.030. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Chest. 2018. PMID: 29108815 Review.
-
Recent Advances in Non-Invasive Blood Pressure Monitoring and Prediction Using a Machine Learning Approach.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Aug 18;22(16):6195. doi: 10.3390/s22166195. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36015956 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sex-related differences in rapid-onset vasodilation: impact of aging.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2021 Jan 1;130(1):206-214. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00663.2020. Epub 2020 Oct 29. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2021. PMID: 33119464 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the haemodynamic effects of high- and low-dose opioid anaesthesia: a secondary analysis of a randomised controlled trial.J Clin Monit Comput. 2024 Dec;38(6):1347-1355. doi: 10.1007/s10877-024-01195-6. Epub 2024 Jul 20. J Clin Monit Comput. 2024. PMID: 39031233 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Remote Patient-Monitoring System for Intensive Care Medicine: Mixed Methods Human-Centered Design and Usability Evaluation.JMIR Hum Factors. 2022 Mar 11;9(1):e30655. doi: 10.2196/30655. JMIR Hum Factors. 2022. PMID: 35275071 Free PMC article.
-
Ringer's lactate administered at 15 °C leads to a greater and more prolonged increase in blood pressure compared to 37 °C.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 26;14(1):25592. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76858-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39462030 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of oscillometric, non-invasive and invasive arterial pressure monitoring in patients undergoing laparoscopic bariatric surgery - a secondary analysis of a prospective observational study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2022 Mar 28;22(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12871-022-01619-3. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022. PMID: 35346046 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cousins TR, O’Donnell JM. Arterial cannulation: a critical review. AANA J 2004; 72: 267–271. - PubMed
-
- Penáz J. Criteria for set point estimation in the volume clamp method of blood pressure measurement. Physiol Res 1992; 41: 5–10. - PubMed
-
- Dorlas JC, Nijboer JA, Butijn WT, et al. Effects of peripheral vasoconstriction on the blood pressure in the finger, measured continuously by a new noninvasive method (the Finapres). Anesthesiology 1985; 62: 342–345. - PubMed
-
- Wesseling KH, de Wit B, van der Hoeven GM. Physiocal, calibrating finger vascular physiology for Finapres. Homeostasis 1995; 36: 67–82.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

