Allele-specific marker-based assessment revealed that the rice blast resistance genes Pi2 and Pi9 have not been widely deployed in Chinese indica rice cultivars
- PMID: 27142801
- PMCID: PMC4854853
- DOI: 10.1186/s12284-016-0091-8
Allele-specific marker-based assessment revealed that the rice blast resistance genes Pi2 and Pi9 have not been widely deployed in Chinese indica rice cultivars
Abstract
Background: The most sustainable approach to control rice blast disease is to develop durably resistant cultivars. In molecular breeding for rice blast resistance, markers developed based on polymorphisms between functional and non-functional alleles of resistance genes, can provide precise and accurate selection of resistant genotypes without the need for difficult, laborious and time-consuming phenotyping. The Pi2 and Pi9 genes confer broad-spectrum resistance against diverse blast isolates. Development of allele-specific markers for Pi2 and Pi9 would facilitate breeding of blast resistant rice by using the two blast resistance genes.
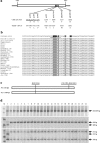
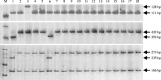
Result: In this work, we developed two new markers, named Pi9-Pro and Pi2-LRR respectively, targeting the unique polymorphisms of the resistant and susceptible alleles of Pi2 and of Pi9. The InDel marker Pi9-Pro differentiates three different genotypes corresponding to the Pi2/Piz-t, Pi9 and non-Pi2/Piz-t/Pi9 alleles, and the CAPS marker Pi2-LRR differentiates the Pi2 allele from the non-Pi2 allele. Based on the two newly developed markers and two available markers Pi2SNP and Pi9SNP, the presence of Pi2 and Pi9 was assessed in a set of 434 rice accessions consisting of 377 Chinese indica cultivars/breeding materials and 57 Chinese japonica cultivars/breeding materials. Of the 434 accessions tested, while one indica restorer line Huazhan was identified harboring the Pi2 resistance allele, no other rice line was identified harboring the Pi2 or Pi9 resistance alleles.
Conclusions: Allele-specific marker-based assessment revealed that Pi2 and Pi9 have not been widely incorporated into diverse Chinese indica rice cultivars. Thus, the two blast resistance genes can be new gene sources for developing blast resistant rice, especially indica rice, in China. The two newly developed markers should be highly useful for using Pi2 and Pi9 in marker-assisted selection (MAS) breeding programs.
Keywords: Blast disease; Molecular marker; Pi2; Pi9; Resistance gene; Rice.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploring the Distribution of Blast Resistance Alleles at the Pi2/9 Locus in Major Rice-Producing Areas of China by a Novel Indel Marker.Plant Dis. 2020 Jul;104(7):1932-1938. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-10-19-2187-RE. Epub 2020 May 20. Plant Dis. 2020. PMID: 32432983
-
Identification of Novel Alleles of the Rice Blast-Resistance Gene Pi9 through Sequence-Based Allele Mining.Rice (N Y). 2020 Dec 7;13(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12284-020-00442-z. Rice (N Y). 2020. PMID: 33284383 Free PMC article.
-
The identification of Pi50(t), a new member of the rice blast resistance Pi2/Pi9 multigene family.Theor Appl Genet. 2012 May;124(7):1295-304. doi: 10.1007/s00122-012-1787-9. Epub 2012 Jan 22. Theor Appl Genet. 2012. PMID: 22270148
-
Status on Genetic Resistance to Rice Blast Disease in the Post-Genomic Era.Plants (Basel). 2025 Mar 5;14(5):807. doi: 10.3390/plants14050807. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40094775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Breeding Strategy and Challenges Towards Improvement of Blast Disease Resistance in Rice Crop.Front Plant Sci. 2015 Nov 16;6:886. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00886. eCollection 2015. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26635817 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Knockout of Pi21 by CRISPR/Cas9 and iTRAQ-Based Proteomic Analysis of Mutants Revealed New Insights into M. oryzae Resistance in Elite Rice Line.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jul 2;11(7):735. doi: 10.3390/genes11070735. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32630695 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding Gene-Editing Potential in Crop Improvement with Pangenomes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 18;23(4):2276. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042276. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression Profile of Defense Genes in Rice Lines Pyramided with Resistance Genes Against Bacterial Blight, Fungal Blast and Insect Gall Midge.Rice (N Y). 2018 Jul 13;11(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12284-018-0231-4. Rice (N Y). 2018. PMID: 30006850 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Elite R-Gene Combinations against Blast Disease in Geng Rice Varieties.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 16;24(4):3984. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043984. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835399 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of resistant germplasm containing novel resistance genes at or tightly linked to the Pi2/9 locus conferring broad-spectrum resistance against rice blast.Rice (N Y). 2017 Dec;10(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12284-017-0176-z. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Rice (N Y). 2017. PMID: 28779340 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashkani S, Rafii MY, Shabanimofrad M, Ghasemzadeh A, Ravanfar SA, Latif MA. Molecular progress on the mapping and cloning of functional genes for blast disease in rice (Oryza sativa L.): current status and future considerations. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2016;36:353–367. doi: 10.3109/07388551.2014.961403. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Zheng Y, Wu W, Zhao C. Screening and application of an SSR marker closely linked to Pi-2 (t), a gene resistant to rice blast (In Chinese with English summary) Mol Plant Breed. 2004;2:321–325.
-
- Correa-Victoria F, Martinez C. Breeding rice cultivars with durable blast resistance in colombia. In: Wang GL, Valent B, editors. Advances in genetics, genomics and control of rice blast disease. Netherlands: Springer; 2009. pp. 375–383.
-
- Costanzo S, Jia Y. Sequence variation at the rice blast resistance gene Pi-km locus: implications for the development of allele specific markers. Plant Sci. 2010;178:523–530. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.02.014. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

