Alpha-Galactosidase A p.A143T, a non-Fabry disease-causing variant
- PMID: 27142856
- PMCID: PMC4855861
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-016-0441-z
Alpha-Galactosidase A p.A143T, a non-Fabry disease-causing variant
Abstract
Background: Fabry disease (FD) is an X-linked multisystemic disorder with a heterogeneous phenotype. Especially atypical or late-onset type 2 phenotypes present a therapeutical dilemma.
Methods: To determine the clinical impact of the alpha-Galactosidase A (GLA) p.A143T/ c.427G > A variation, we retrospectively analyzed 25 p.A143T patients in comparison to 58 FD patients with other missense mutations.
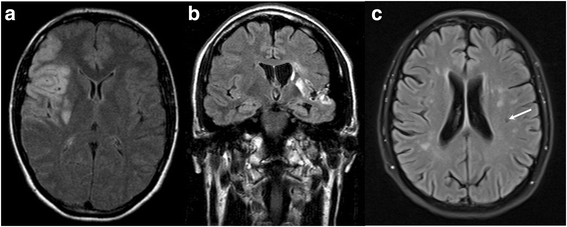
Results: p.A143T patients suffering from stroke/ transient ischemic attacks had slightly decreased residual GLA activities, and/or increased lyso-Gb3 levels, suspecting FD. However, most male p.A143T patients presented with significant residual GLA activity (~50 % of reference), which was associated with normal lyso-Gb3 levels. Additionally, p.A143T patients showed less severe FD-typical symptoms and absent FD-typical renal and cardiac involvement in comparison to FD patients with other missense mutations. Two tested female p.A143T patients with stroke/TIA did not show skewed X chromosome inactivation. No accumulation of neurologic events in family members of p.A143T patients with stroke/transient ischemic attacks was observed.
Conclusions: We conclude that GLA p.A143T seems to be most likely a neutral variant or a possible modifier instead of a disease-causing mutation. Therefore, we suggest that p.A143T patients with stroke/transient ischemic attacks of unknown etiology should be further evaluated, since the diagnosis of FD is not probable and subsequent ERT or chaperone treatment should not be an unreflected option.
Keywords: Fabry disease; GLA mutation; Genotype; Late-onset; Lyso-Gb3; Stroke; Variant of unknown significance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Higher rate of rheumatic manifestations and delay in diagnosis in Brazilian Fabry disease patients.Adv Rheumatol. 2020 Jan 6;60(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s42358-019-0111-7. Adv Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31907047
-
Phenotypical characterization of α-galactosidase A gene mutations identified in a large Fabry disease screening program in stroke in the young.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013 Jul;115(7):1088-93. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2012.11.003. Epub 2012 Dec 4. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013. PMID: 23219219
-
Phenotype and biochemical heterogeneity in late onset Fabry disease defined by N215S mutation.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 5;13(4):e0193550. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193550. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29621274 Free PMC article.
-
Screening for Fabry disease in a series of Parkinson's disease patients and literature review.Neurol Sci. 2023 Apr;44(4):1235-1241. doi: 10.1007/s10072-022-06554-2. Epub 2022 Dec 22. Neurol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36547780 Review.
-
Impact of GLA Variant Classification on the Estimated Prevalence of Fabry Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Screening Studies.Circ Genom Precis Med. 2023 Dec;16(6):e004252. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGEN.123.004252. Epub 2023 Dec 4. Circ Genom Precis Med. 2023. PMID: 38047356
Cited by
-
Fabry disease in the Spanish population: observational study with detection of 77 patients.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2018 Apr 10;13(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s13023-018-0792-8. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2018. PMID: 29631605 Free PMC article.
-
Misprocessing of α -Galactosidase A, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and the Unfolded Protein Response.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2025 Apr 1;36(4):628-644. doi: 10.1681/ASN.0000000535. Epub 2024 Nov 12. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39704415
-
Fabry disease and kidney involvement: starting from childhood to understand the future.Pediatr Nephrol. 2022 Jan;37(1):95-103. doi: 10.1007/s00467-021-05076-x. Epub 2021 Apr 30. Pediatr Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 33928440 Review.
-
X-chromosomal inactivation patterns in women with Fabry disease.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2022 Sep;10(9):e2029. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.2029. Epub 2022 Aug 16. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2022. PMID: 35971858 Free PMC article.
-
Challenging the traditional approach for interpreting genetic variants: Lessons from Fabry disease.Clin Genet. 2022 Apr;101(4):390-402. doi: 10.1111/cge.14102. Epub 2021 Dec 28. Clin Genet. 2022. PMID: 34927718 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mehta A, Ricci R, Widmer U, Dehout F, Garcia de Lorenzo A, Kampmann C, Linhart A, Sunder-Plassmann G, Ries M, Beck M. Fabry disease defined: baseline clinical manifestations of 366 patients in the Fabry Outcome Survey. Eur J Clin Invest. 2004;34:236–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2004.01309.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Oliveira JP, Ferreira S, Reguenga C, Carvalho F, Månsson JE. The g.1170C > T polymorphism of the 5’ untranslated region of the human alpha-galactosidase gene is associated with decreased enzyme expression--evidence from a family study. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2008;31:S405–S413. doi: 10.1007/s10545-008-0972-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rombach SM, Dekker N, Bouwman MG, Linthorst GE, Zwinderman AH, Wijburg FA, Kuiper S, Vd Bergh Weerman MA, Groener JE, Poorthuis BJ, Hollak CE, Aerts JM. Plasma globotriaosylsphingosine: diagnostic value and relation to clinical manifestations of Fabry disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1802:741–748. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.05.003. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

