Differential Type I Interferon Signaling Is a Master Regulator of Susceptibility to Postinfluenza Bacterial Superinfection
- PMID: 27143388
- PMCID: PMC4959663
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00506-16
Differential Type I Interferon Signaling Is a Master Regulator of Susceptibility to Postinfluenza Bacterial Superinfection
Abstract
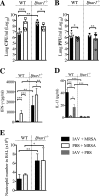
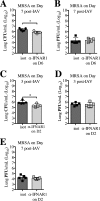
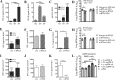
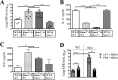
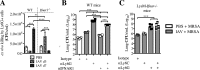
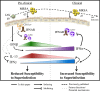
Bacterial superinfections are a primary cause of death during influenza pandemics and epidemics. Type I interferon (IFN) signaling contributes to increased susceptibility of mice to bacterial superinfection around day 7 post-influenza A virus (IAV) infection. Here we demonstrate that the reduced susceptibility to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) at day 3 post-IAV infection, which we previously reported was due to interleukin-13 (IL-13)/IFN-γ responses, is also dependent on type I IFN signaling and its subsequent requirement for protective IL-13 production. We found, through utilization of blocking antibodies, that reduced susceptibility to MRSA at day 3 post-IAV infection was IFN-β dependent, whereas the increased susceptibility at day 7 was IFN-α dependent. IFN-β signaling early in IAV infection was required for MRSA clearance, whereas IFN-α signaling late in infection was not, though it did mediate increased susceptibility to MRSA at that time. Type I IFN receptor (IFNAR) signaling in CD11c(+) and Ly6G(+) cells was required for the observed reduced susceptibility at day 3 post-IAV infection. Depletion of Ly6G(+) cells in mice in which IFNAR signaling was either blocked or deleted indicated that Ly6G(+) cells were responsible for the IFNAR signaling-dependent susceptibility to MRSA superinfection at day 7 post-IAV infection. Thus, during IAV infection, the temporal differences in type I IFN signaling increased bactericidal activity of both CD11c(+) and Ly6G(+) cells at day 3 and reduced effector function of Ly6G(+) cells at day 7. The temporal differential outcomes induced by IFN-β (day 3) and IFN-α (day 7) signaling through the same IFNAR resulted in differential susceptibility to MRSA at 3 and 7 days post-IAV infection.
Importance: Approximately 114,000 hospitalizations and 40,000 annual deaths in the United States are associated with influenza A virus (IAV) infections. Frequently, these deaths are due to community-acquired Gram-positive bacterial species, many of which show increasing resistance to antibiotic therapy. Severe complications, including parapneumonic empyema and necrotizing pneumonia, can arise, depending on virulence factors expressed by either the virus or bacteria. Unfortunately, we are unable to control the expression of these virulence factors, making host responses a logical target for therapeutic interventions. Moreover, interactions between virus, host, and bacteria that exacerbate IAV-related morbidities and mortalities are largely unknown. Here, we show that type I interferon (IFN) expression can modulate susceptibility to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection, with IFN-β reducing host susceptibility to MRSA infection while IFN-α increases susceptibility. Our data indicate that treatments designed to augment IFN-β and/or inhibit IFN-α production around day 7 post-IAV infection could reduce susceptibility to deadly superinfections.
Copyright © 2016 Shepardson et al.
Figures


Similar articles
-
IFNAR2 Is Required for Anti-influenza Immunity and Alters Susceptibility to Post-influenza Bacterial Superinfections.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 9;9:2589. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02589. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30473701 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of IFN-γ by IL-13 dictates susceptibility to secondary postinfluenza MRSA pneumonia.Eur J Immunol. 2014 Nov;44(11):3263-72. doi: 10.1002/eji.201444582. Epub 2014 Sep 1. Eur J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25091976 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Role for PDZ-Binding Motif of Influenza A Virus Nonstructural Protein 1 in Regulation of Host Susceptibility to Postinfluenza Bacterial Superinfections.Viral Immunol. 2019 Apr;32(3):131-143. doi: 10.1089/vim.2018.0118. Epub 2019 Mar 1. Viral Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30822217 Free PMC article.
-
Influenza and Bacterial Superinfection: Illuminating the Immunologic Mechanisms of Disease.Infect Immun. 2015 Oct;83(10):3764-70. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00298-15. Epub 2015 Jul 27. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 26216421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel pandemic influenza A (H1N1) and community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2015 Feb;13(2):197-207. doi: 10.1586/14787210.2015.999668. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2015. PMID: 25578884 Review.
Cited by
-
IFNAR2 Is Required for Anti-influenza Immunity and Alters Susceptibility to Post-influenza Bacterial Superinfections.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 9;9:2589. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02589. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30473701 Free PMC article.
-
Time-Dependent Increase in Susceptibility and Severity of Secondary Bacterial Infections During SARS-CoV-2.Front Immunol. 2022 May 12;13:894534. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.894534. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35634338 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Type I and III Interferons on Respiratory Superinfections Due to Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens.J Infect Dis. 2017 Feb 15;215(suppl_1):S58-S63. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw466. J Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28375519 Free PMC article.
-
IFN Receptor 2 Regulates TNF-α-Mediated Damaging Inflammation during Aspergillus Pulmonary Infection.J Immunol. 2024 Oct 15;213(8):1202-1211. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200686. J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39212415
-
Exposing the Two Contrasting Faces of STAT2 in Inflammation.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2022 Sep;42(9):467-481. doi: 10.1089/jir.2022.0117. Epub 2022 Jul 25. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2022. PMID: 35877097 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

