The ABC of Ribosome-Related Antibiotic Resistance
- PMID: 27143393
- PMCID: PMC4959660
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00598-16
The ABC of Ribosome-Related Antibiotic Resistance
Abstract
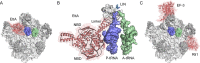
The increase in multidrug-resistant pathogenic bacteria is limiting the utility of our current arsenal of antimicrobial agents. Mechanistically understanding how bacteria obtain antibiotic resistance is a critical first step to the development of improved inhibitors. One common mechanism for bacteria to obtain antibiotic resistance is by employing ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters to actively pump the drug from the cell. The ABC-F family includes proteins conferring resistance to a variety of clinically important ribosome-targeting antibiotics; however, controversy remains as to whether resistance is conferred via efflux like other ABC transporters or whether another mechanism, such as ribosome protection, is at play. A recent study by Sharkey and coworkers (L. K. Sharkey, T. A. Edwards, and A. J. O'Neill, mBio 7:e01975-15, 2016, http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01975-15) provides strong evidence that ABC-F proteins conferring antibiotic resistance utilize ribosome protection mechanisms, namely, by interacting with the ribosome and displacing the drug from its binding site, thus revealing a novel role for ABC-F proteins in antibiotic resistance.
Copyright © 2016 Wilson.
Figures
Comment on
-
ABC-F Proteins Mediate Antibiotic Resistance through Ribosomal Protection.mBio. 2016 Mar 22;7(2):e01975. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01975-15. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27006457 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
