Evaluation of serum lipid profile, body mass index, and waistline in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 27143868
- PMCID: PMC4841420
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S104803
Evaluation of serum lipid profile, body mass index, and waistline in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Objective: People with type 2 diabetes are at an increased risk of hypertension, arteriosclerosis, heart disease, and stroke. Glucose intolerance (insulin resistance) is the main feature of type 2 diabetes. Obesity leads to insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, etc. The aim of this study was to assess the biochemical parameters and measures of obesity in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods: A total of 2,273 males and 6,547 females previously healthy volunteers (aged 41-95 years old) were recruited by open invitation. The basic information, including age, sex, height, weight, body mass index (BMI), waistline, hipline, menstrual cycle, and medical history, was collected by questionnaire survey and physical examination. Serum lipid profile, liver transaminase, blood glucose, postprandial blood glucose, and hemoglobin A1c were obtained after 12 hours of fasting.
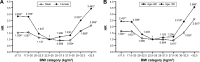
Results: According to our results, diabetic patients presented serum lipid abnormality. Elevated triglyceride (TG) levels (≥1.7 mmol/L) were noted in 19.69% of males and 20.40% of females, and reduced high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels (≤1.15 mmol/L) were noted in 21.96% of males and 15.74% of females. The combination of elevated TG and reduced HDL-C was the most prevalent of the combined lipid abnormalities. In contrast, no differences were observed in the levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and total cholesterol. Moreover, there were statistically significant differences in the levels of BMI and waistline between T2DM and non-T2DM participants. After adjustment for BMI, logistic regression analysis revealed that the subjects with BMI ≤20 kg/m(2) and >30 kg/m(2) had a significantly elevated hazard ratio of T2DM compared with participants having a BMI range of 20-30 kg/m(2) in both males and females. However, there was a significant difference between T2DM patients and non-T2DM patients in waistline (χ (2)=8.57, P<0.001) than in BMI parameter (χ (2)=6.29, P<0.001).
Conclusion: The present study shows for the first time that low levels of HDL-C, high levels of TG, and abnormal levels in BMI and waistline increase the risk of type 2 T2DM in Chinese people.
Keywords: HDL-C; T2DM; TG; body mass index; risk assessment; waistline.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment risk of osteoporosis in Chinese people: relationship among body mass index, serum lipid profiles, blood glucose, and bone mineral density.Clin Interv Aging. 2016 Jul 4;11:887-95. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S103845. eCollection 2016. Clin Interv Aging. 2016. PMID: 27445467 Free PMC article.
-
Value of simple clinical parameters to predict insulin resistance among newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes in limited resource settings.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 31;16(3):e0248469. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248469. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33788827 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the Ratio of Triglycerides to High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels with the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Study in Beijing.J Diabetes Res. 2021 Apr 20;2021:5524728. doi: 10.1155/2021/5524728. eCollection 2021. J Diabetes Res. 2021. PMID: 33969127 Free PMC article.
-
ANGPTL3 as a target for treating lipid disorders in type 2 diabetes patients.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Nov 1;23(1):356. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02352-1. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39487451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between triglyceride to HDL cholesterol ratio and a risk of diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lab Med. 2025 Jan 6;56(1):1-6. doi: 10.1093/labmed/lmae052. Lab Med. 2025. PMID: 39066659
Cited by
-
Multivariate analysis of genomics data to identify potential pleiotropic genes for type 2 diabetes, obesity and dyslipidemia using Meta-CCA and gene-based approach.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 15;13(8):e0201173. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201173. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30110382 Free PMC article.
-
Pioglitazone does not increase the risk of type II diabetes in patients with bladder cancer: A retrospective study.Oncol Lett. 2016 Jul;12(1):89-92. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4566. Epub 2016 May 13. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27347105 Free PMC article.
-
Dyslipidaemia was correlated to the posterior circulation infarction in non-diabetic populations.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Jun 26;17(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0799-0. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 29945627 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship of 25(OH)D3 with Diabetes Mellitus and the Mediation Effect of Lipid Profile in Chinese Rural Population of Henan Province.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Jan 6;58(1):85. doi: 10.3390/medicina58010085. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35056393 Free PMC article.
-
Dyslipidemia Among Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Case-Control Study From a Tertiary Care Hospital in South India.Cureus. 2023 Feb 28;15(2):e35625. doi: 10.7759/cureus.35625. eCollection 2023 Feb. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37007365 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Ogden CL. Prevalence of obesity and trends in the distribution of body mass index among US adults, 1999–2010. JAMA. 2012;307(5):491–497. - PubMed
-
- de Wilde JA, Zandbergen-Harlaar S, van Buuren S, Middelkoop BJ. Trends in body mass index distribution and prevalence of thinness, overweight and obesity in two cohorts of Surinamese South Asian children in The Netherlands. Arch Dis Child. 2013;98(4):280–285. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

